The volatile nature of cryptocurrency markets demands robust strategies for portfolio protection. Understanding and implementing crypto hedging can significantly mitigate downside risk, allowing for more stable long-term investment. This guide explores the mechanics, strategies, and psychological aspects of effectively hedging your digital assets.
While understanding Crypto Hedging is important, applying that knowledge is where the real growth happens. Create Your Free Crypto Trading Account to practice with a free demo account and put your strategy to the test.
What is crypto hedging?
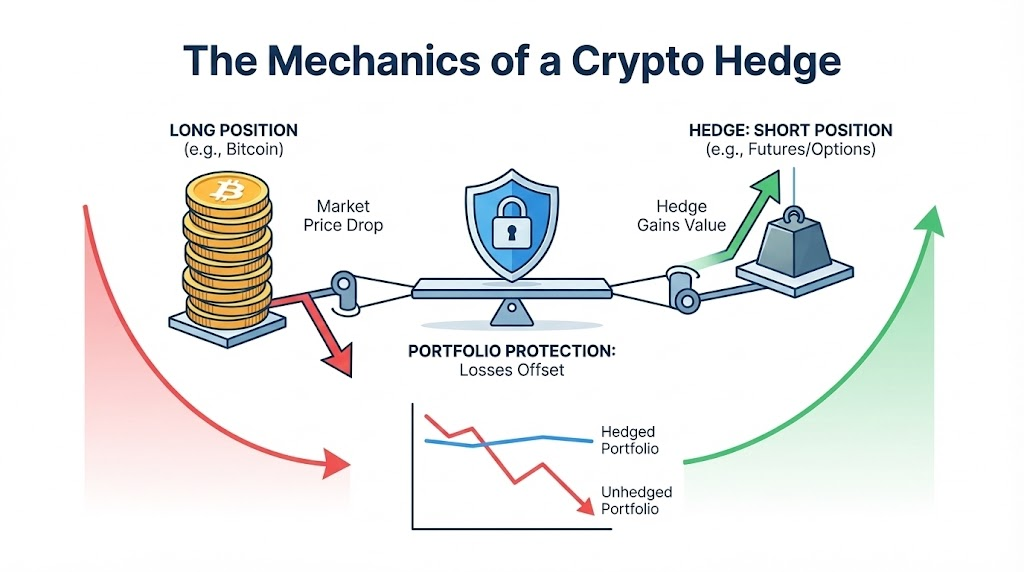
Crypto hedging is the practice of using financial instruments (stocks, forex, crypto) to offset the risk of adverse price movements in a cryptocurrency asset, as defined by OSL. It involves taking a position in a related asset or derivative that is expected to move in the opposite direction of your primary holding. This strategy aims to reduce potential losses from unexpected price drops, acting as a form of insurance against market volatility.
Why is hedging essential in crypto markets?
Hedging is essential in crypto markets due to their extreme volatility, which can lead to rapid and significant price swings. Implementing hedging strategies helps with risk management by protecting a portfolio from sudden downturns, preserving capital, and reducing emotional stress during uncertain periods.
This approach is vital for portfolio protection, enabling investors to maintain long-term positions without constant exposure to unmitigated downside risk.
The Fundamentals of Risk Management in Crypto Hedging
Risk management in crypto hedging centers on taking an opposite position to your existing crypto assets to counteract potential losses. If you hold Bitcoin and anticipate a temporary price decline, you might open a short position on Bitcoin derivatives. This short position gains value if Bitcoin’s price falls, offsetting some or all of the losses from your spot market holdings. The core principle is to manage exposure to market volatility by creating a balanced risk profile, rather than seeking direct profit from the hedge itself. It is a strategic approach to maintain portfolio protection against adverse price movements.
Why Hedge Your Crypto Portfolio?
Hedging a crypto portfolio offers several key benefits, primarily focusing on portfolio protection and mitigating the impact of volatility. It helps preserve capital during market downturns, preventing significant losses that could otherwise erode investment value. Hedging reduces the emotional stress associated with unpredictable market swings, allowing investors to make more rational decisions.
This strategy also enables long-term holding of promising assets by providing a safety net, making it possible to ride out bear markets while keeping core positions intact.
The Risks of Crypto Hedging: What Could Go Wrong?
Hedging, while beneficial, carries its own set of risks, often leading to common pitfalls for traders. Basis risk is a significant concern, referring to the potential for the price of the hedging instrument not to perfectly correlate with the underlying asset, leading to imperfect protection.
Execution risk involves the difficulty of accurately timing and placing trades, especially in fast-moving markets with varying liquidity. Additionally, hedging involves costs such as trading fees, funding rates for perpetual swaps, and potential margin call risks in margin trading, which can erode overall returns.
Users sometimes lose money trying to hedge with futures due to miscalculating position sizes or underestimating the impact of funding rates. These complexities highlight why thorough understanding and careful planning are critical to effective risk management.
Ready to Elevate Your Trading?
You have the information. Now, get the platform. Join thousands of successful traders who use Volity for its powerful tools, fast execution, and dedicated support.
Create Your Account in Under 3 MinutesTop Crypto Hedging Strategies & Their Mechanisms
Derivatives: The Core of Crypto Hedging
Derivatives are financial contracts that derive their value from an underlying asset, such as a cryptocurrency. They are fundamental to hedging strategies because they allow traders to speculate on price movements without owning the actual asset. Professional traders often use derivatives like futures, options, and perpetual swaps to take opposing positions to their spot holdings.
These instruments provide the flexibility and leverage needed to effectively offset potential losses, making them indispensable tools for sophisticated risk management in volatile crypto markets.
Futures Contracts: Locking in Future Prices
Futures contracts are agreements to buy or sell a specified cryptocurrency at a predetermined price on a future date. They are a common method for hedging Bitcoin risk and other digital assets. If an investor holds Bitcoin and fears a price drop, they can sell a Bitcoin futures contract.
If the price falls, the loss on their spot Bitcoin is offset by the profit from the short futures position. The ability to lock in future prices makes futures a powerful tool for managing price exposure, especially for miners or institutions needing to secure future revenue streams.
Options Contracts: Limiting Downside with Flexibility
Options contracts provide the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying cryptocurrency at a specific price (strike price) before a certain expiry date. Put options are particularly useful for hedging, as they give the holder the right to sell an asset at the strike price.
If you own Ethereum and buy a put option, your downside risk protection is limited to the strike price, regardless of how far Ethereum’s market price falls. This strategy offers flexibility by limiting potential losses while preserving upside potential if the market rises.
Perpetual Swaps: Continuous Hedging without Expiry
Perpetual swaps are a type of futures contract without an expiry date, making them highly popular in crypto markets for continuous hedging. These contracts track the underlying asset’s price, with a mechanism called funding rates keeping the swap price close to the spot price. Traders can use perpetual swaps to maintain a long or short position indefinitely, adjusting their leverage as needed.
This allows for flexible and ongoing crypto hedging without the need for frequent rollovers, though constant monitoring of funding rates is essential.
Short Selling: Direct Bet Against Price
Short selling involves borrowing a cryptocurrency, selling it on the open market, and then buying it back later at a lower price to return to the lender, profiting from the price difference. This is a direct method to hedge against price declines. For instance, if an investor believes the price of a specific altcoin will fall, they can short sell it to offset potential losses in their existing long position. While simpler than derivatives, short selling typically requires a margin account and carries the risk of unlimited losses if the price rises unexpectedly.
Dynamic Hedging: Real-Time Risk Adjustment
Dynamic hedging is an advanced strategy that involves continuously adjusting hedging positions in real time to adapt to changing market conditions. As highlighted by Amberdata, dynamic hedging strategies for crypto involve real-time risk adjustment to market conditions. This approach is particularly effective in highly volatile markets where static hedges can quickly become ineffective. It often utilizes algorithms and automated systems to maintain a desired risk exposure, such as a delta neutral strategy, making sure that the portfolio remains protected against small price movements by constantly rebalancing positions.
Systematic Hedging: Rule-Based Portfolio Protection
Systematic hedging employs a rule-based approach to portfolio protection, contrasting with the more discretionary nature of dynamic hedging. This strategy relies on predefined rules and quantitative models to execute hedges automatically, often based on factors like correlation coefficient between assets or specific market indicators.
QuantPedia notes that systematic hedging of cryptocurrency portfolios can improve risk management through structured, automated processes. This method aims to remove emotional biases from hedging decisions, making sure consistent application of risk management principles even in rapidly changing markets.
Comparison of Hedging Instruments & Their Suitability
| Strategy | Mechanism | Pros | Cons | Best For | Complexity |
| Futures | Agreement to buy/sell at set future price | Price lock-in, leverage | Expiry risk, margin calls | Large portfolios, price discovery | Moderate |
| Options | Right, not obligation, to buy/sell | Limited downside, flexible | Premiums, expiry risk | Tailored risk, specific events | High |
| Perpetual Swaps | Futures without expiry | Continuous, high liquidity | Funding fees, liquidation | Active traders, continuous hedge | Moderate |
| Short Selling | Borrow & sell, buy back lower | Direct bet on price fall | Unlimited loss potential | Simple downside hedge | Low |
Crypto Hedging Challenges & User Pain Points
The risk of stablecoin de-pegging has emerged as a significant concern in the crypto market, posing a new challenge for risk management. While traditional hedging aims to protect against volatility in volatile assets, stablecoin de-pegging is a risk against the “stable” component itself. Strategies for hedging this specific risk are limited and complex.

Some approaches might involve diversifying stablecoin holdings across multiple issuers or using stablecoin conversion to different fiat-backed stablecoins if a de-peg event is anticipated. For users asking, “My stablecoin lost its peg, can hedging prevent this?”, the answer is often difficult as direct hedging instruments against de-pegging are scarce, emphasizing due diligence in stablecoin selection.
Is Hedging Profitable?
Hedging is primarily a risk management tool, not a direct profit-generating strategy. Its purpose is to reduce or offset potential losses from adverse price movements in an underlying asset. Therefore, a successful hedge typically results in a smaller loss than if no hedge were in place, or it prevents a loss entirely.
However, hedging incurs costs such as trading fees, premiums for options, and funding rates for perpetual swaps. These costs mean that hedging can reduce overall net outcomes, even in a stable or rising market. The “profit” from hedging comes from the capital preserved and the avoidance of significant losses, functioning more like an insurance premium rather than an investment return.
The Psychology of Hedging: Managing Emotions in Volatile Markets
Psychological factors can account for a significant portion of trading losses, often leading to suboptimal hedging decisions due to fear or greed, as noted by Openware. Emotions like fear can cause premature exits from positions or panicked hedging, while greed can lead to over-leveraging or neglecting to hedge at all. Effectively managing emotional trading when markets are volatile is critical for maintaining a sound hedging strategy.
Developing a disciplined approach, adhering to a predefined risk management plan, and understanding the long-term benefits of capital preservation over short-term gains are essential. By acknowledging and controlling these psychological biases, traders can make more rational decisions, reinforcing the effectiveness of their hedges.
A Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing Hedging
Implementing a crypto hedging strategy involves several practical steps to make sure effective risk management. First, assess your current portfolio’s exposure and your risk tolerance. Next, choose an appropriate hedging strategy based on your assets, market outlook, and available instruments.
Then, select a suitable platform that offers the necessary hedging tools, whether it’s a centralized or decentralized exchange. Execute your chosen hedge, making sure correct position sizing and understanding associated costs. Finally, continuously monitor your hedge and market conditions, adjusting your strategy as needed to maintain optimal portfolio protection.
Choosing the Right Platform for Hedging
Choosing the right platform for crypto hedging depends on your preferred instruments, experience level, and risk appetite. Centralized Exchanges (CEXs) like Binance or Coinbase offer a wide range of derivatives, higher liquidity, and user-friendly interfaces, making them popular for futures and options trading.
Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), which include platforms using automated market makers, provide greater autonomy and often access to novel instruments, though they may have lower liquidity and higher complexity. Factors to consider include trading fees, available leverage, geographic restrictions, and the security reputation of the platform.
Tailoring Your Strategy to Your Portfolio and Goals
Tailoring your hedging strategy to your specific portfolio and investment goals is crucial for effective risk management. For smaller portfolios, the costs associated with hedging might outweigh the benefits, making simpler methods like holding a portion in stablecoins or focusing on portfolio diversification more appropriate.
Larger portfolios might benefit from more complex derivatives like options or perpetual futures contracts to manage substantial exposure. Your risk tolerance dictates the aggressiveness of your hedge; conservative investors might opt for full hedges, while those comfortable with more risk might implement partial hedges.
Turn Knowledge into Profit
You've done the reading, now it's time to act. The best way to learn is by doing. Open a free, no-risk demo account and practice your strategy with virtual funds today.
Open a Free Demo AccountBOTTOM LINE
Crypto hedging is the ultimate defense mechanism for the modern digital investor, transforming market volatility from a catastrophic threat into a manageable variable. While no hedge is entirely cost-free, the price of protection is far lower than the cost of unmitigated liquidation. Success in this arena requires a transition from a ‘hope-based’ strategy to one rooted in mathematical risk offsets and emotional detachment. By mastering instruments like perpetual swaps and put options, you secure your portfolio’s longevity, ensuring that you remain solvent long enough to capitalize on the market’s eventual recovery.
Key Takeaways
- Hedging as Asset Protection: Spot trading grants direct ownership, but hedging provides the necessary insurance to keep those assets through downturns.
- Derivatives are Essential: Instruments like futures, options, and perpetual swaps are the primary tools for professional risk management.
- Psychology Over Profits: The goal of hedging is capital preservation and emotional stability, not direct speculative gain.
- Dynamic Adjustment: Effective hedging requires ongoing monitoring of funding rates and market correlations to remain effective.






