Central banks significantly shape gold prices through monetary policy, reserve management, and responses to global economic shifts. This guide explores how their actions, from interest rate adjustments to strategic reserve purchases, directly impact gold’s appeal as a safe haven asset. You will learn to identify key central bank influences and better navigate the complex dynamics of the gold market.
While understanding Central Banks Influence Gold Prices is important, applying that knowledge is where the real growth happens. Create Your Free Forex Trading Account to practice with a free demo account and put your strategy to the test.
How do central banks influence gold prices?

Central banks exert influence on gold prices through various channels, primarily their monetary policy decisions and the management of national gold reserves. These actions can directly impact gold’s appeal as an investment and its role as a safe haven asset. The aggregate behavior of central banks, particularly their buying and selling patterns, sends strong signals to the global market.
Why do central banks hold gold?
Central banks hold gold as a strategic reserve asset for several fundamental reasons, moving beyond simple monetary policy. Gold serves as a reliable store of value, particularly during periods of economic instability or fiat currency depreciation. It acts as a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation, preserving national wealth.
Furthermore, gold provides portfolio diversification for foreign exchange reserves, reducing reliance on any single currency, such as the US dollar. Central banks globally have been net buyers of gold for 14 consecutive years, with 2022 and 2023 seeing record purchases, highlighting gold’s strategic importance as a reserve asset amidst economic uncertainty. While most central banks are accumulating gold, some may sell for specific reasons like funding emergencies or rebalancing reserves, but the overarching trend points to increased holdings.
National Economic Stability
Gold holdings contribute significantly to a nation’s economic stability, especially during times of crisis. Gold’s high liquidity and universal acceptance bolster confidence in a country’s financial health. When traditional financial systems face stress, gold provides a tangible asset that can be mobilized. Investors often question if gold remains a safe haven in today’s central bank environment. Its appeal strengthens during geopolitical instability or periods of high inflation, prompting central banks and institutional investors alike to increase their gold reserves.
What are the main tools central banks use to affect gold?
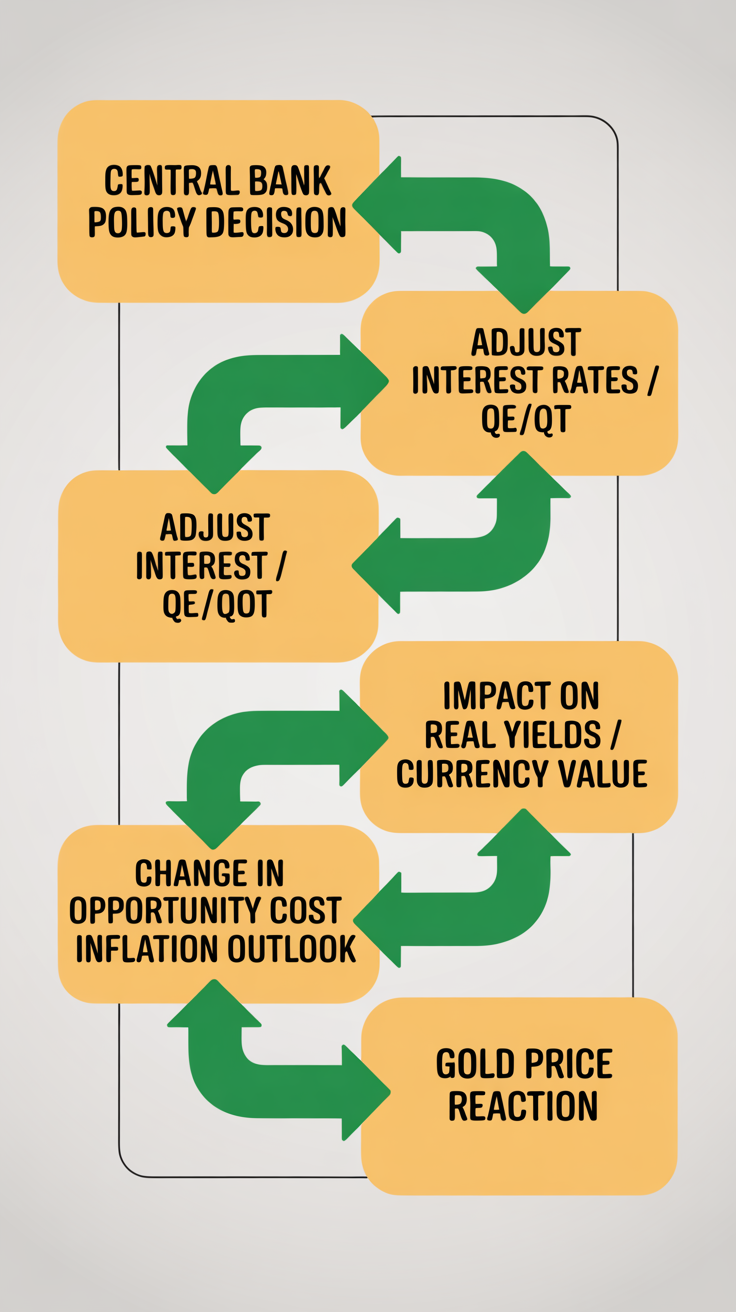
Central banks employ a range of monetary policy tools designed to manage their national economies, which in turn have profound effects on gold prices. These tools, while not directly targeting gold, influence macroeconomic conditions that dictate gold’s attractiveness to investors. The primary mechanisms include setting interest rates and implementing quantitative easing or tightening programs. Understanding these policies is crucial for discerning gold’s price trajectory.
The Influence of Monetary Policy on Gold
Monetary policy encompasses the actions undertaken by a central bank to influence the availability and cost of money and credit to help promote national economic goals. These goals typically include maintaining price stability, maximizing employment, and building moderate long-term interest rates. When central banks adjust their monetary policy, they create ripple effects across financial markets, with gold prices often reacting significantly.
What is the relationship between interest rates and gold prices?
The relationship between interest rates and gold prices is typically inverse. Gold is a non-yielding asset, meaning it does not pay dividends or interest. When central banks raise interest rates, particularly real interest rates (nominal rates adjusted for inflation), the opportunity cost of holding gold increases. Investors are more likely to choose interest-bearing assets, such as government bonds, over gold because they can earn a higher return. Higher real interest rates, influenced by central bank monetary policy, typically increase the opportunity cost of holding non-yielding assets like gold, often leading to downward pressure on gold prices. Conversely, when central banks lower interest rates, the opportunity cost of holding gold decreases, making it more appealing.
| Gold | High Rates | High | Negative |
| Gold | Low Rates | Low | Positive |
| Interest-Bearing | High Rates | Lower Appeal | N/A |
| Interest-Bearing | Low Rates | Higher Appeal | N/A |
How does quantitative easing (QE) or tightening (QT) affect gold?
Quantitative Easing (QE) programs involve central banks purchasing large quantities of government bonds and other financial assets from the open market. This action expands the money supply, injects liquidity into the financial system, and aims to lower long-term interest rates. By increasing the money supply, QE can potentially devalue fiat currencies and stir fears of inflation. In such an environment, investors, including central banks, often turn to gold as an inflation hedge and a safe haven asset, driving gold prices higher. The opposite effect is observed during Quantitative Tightening (QT), where central banks reduce their balance sheets by selling assets or allowing them to mature without reinvestment. QT removes liquidity from the system, potentially strengthening the currency and increasing real yields, which can exert dampening pressure on gold.
Ready to Elevate Your Trading?
You have the information. Now, get the platform. Join thousands of successful traders who use Volity for its powerful tools, fast execution, and dedicated support.
Create Your Account in Under 3 MinutesDoes inflation affect gold prices?
Inflation has a significant impact on gold prices, largely due to gold’s traditional role as an inflation hedge. When the purchasing power of fiat currencies eroding due to rising prices, gold tends to retain its value or even appreciate. The expectation of future inflation can prompt increased demand for gold, pushing prices upward. Central banks aim to control inflation through their monetary policy decisions, such as adjusting interest rates. If central banks are perceived as being ineffective in managing inflation, or if inflation rises unexpectedly, gold’s appeal as a protective asset typically increases.
What role does the US dollar play in central bank gold decisions?
The U.S. dollar plays a pivotal role in central bank gold decisions and global gold prices due to its status as the world’s primary reserve currency and the currency in which gold is typically denominated. A stronger US dollar makes gold more expensive for holders of other currencies, effectively reducing demand and putting downward pressure on gold prices. The U.S. Dollar’s strength often has an inverse relationship with gold prices, as gold is priced in dollars; a stronger dollar makes gold more expensive for holders of other currencies, dampening demand. Central banks, when managing their foreign exchange reserves, consider the currency value of the dollar in relation to their gold holdings. A desire to diversify away from heavy dollar reliance, often motivated by geopolitical or economic concerns, can lead central banks to increase their gold reserves, thereby influencing global gold prices.
How do central bank gold purchases impact global prices?
Large-scale gold purchases by central banks significantly impact global gold prices by directly affecting market supply and demand dynamics. When central banks enter the market as substantial buyers, they absorb available supply, which can create upward pressure on prices. This official sector demand also signals confidence in gold as a reserve asset, encouraging other institutional and retail investors. The sustained buying trend observed in recent years demonstrates this influence. Central banks globally have been net buyers of gold for 14 consecutive years, with 2022 and 2023 seeing record purchases, highlighting gold’s strategic importance as a reserve asset amidst economic uncertainty. Conversely, large-scale sales, though less common currently, could flood the market and depress prices.
What happens to gold when central banks sell reserves?
When central banks sell gold reserves, it typically indicates a shift in their strategic priorities or an urgent need for liquidity. While current trends show net buying, historical instances of central bank gold sales have often led to downward pressure on gold prices. Such sales increase the supply of gold on the market, and if the volume is substantial, it can outweigh demand, leading to price declines. However, central banks are generally cautious to avoid market disruption, often executing sales discreetly or over extended periods. Motivations for selling can include funding national emergencies, rebalancing foreign exchange reserves to favor other assets, or responding to specific economic stability concerns.
Are central bank gold reserves a good indicator for investors?
Central bank gold reserves can serve as an indicator for investors, signaling broader trends in global finance and economic sentiment. The continued accumulation of gold by central banks, especially during periods of geopolitical risks and market volatility, suggests a collective belief in gold’s enduring value as a safe haven asset. This can provide a degree of reassurance for individual investors considering gold for their portfolios. However, interpreting central bank actions requires nuance. Central banks operate on much longer time horizons and with different objectives than most retail investors. Their decisions are influenced by complex factors, including national economic stability, sovereign debt levels, and sanctions risk, which may not directly translate to short-term gold price movements.
📌 REMEMBER: While central bank gold movements provide a macro signal, individual investors must consider their own financial goals and risk tolerance.
| United States | 8,133.5 | 68.2% |
| Germany | 3,352.6 | 68.9% |
| Italy | 2,451.8 | 68.6% |
| France | 2,436.9 | 65.4% |
| Russia | 2,332.7 | 26.1% |
| China | 2,262.5 | 4.3% |
| Switzerland | 1,040.0 | 6.4% |
| Japan | 846.0 | 4.4% |
| India | 822.9 | 8.2% |
| Netherlands | 612.5 | 58.7% |
Data as of December 2023, sourced from World Gold Council.
Beyond Economic Policy
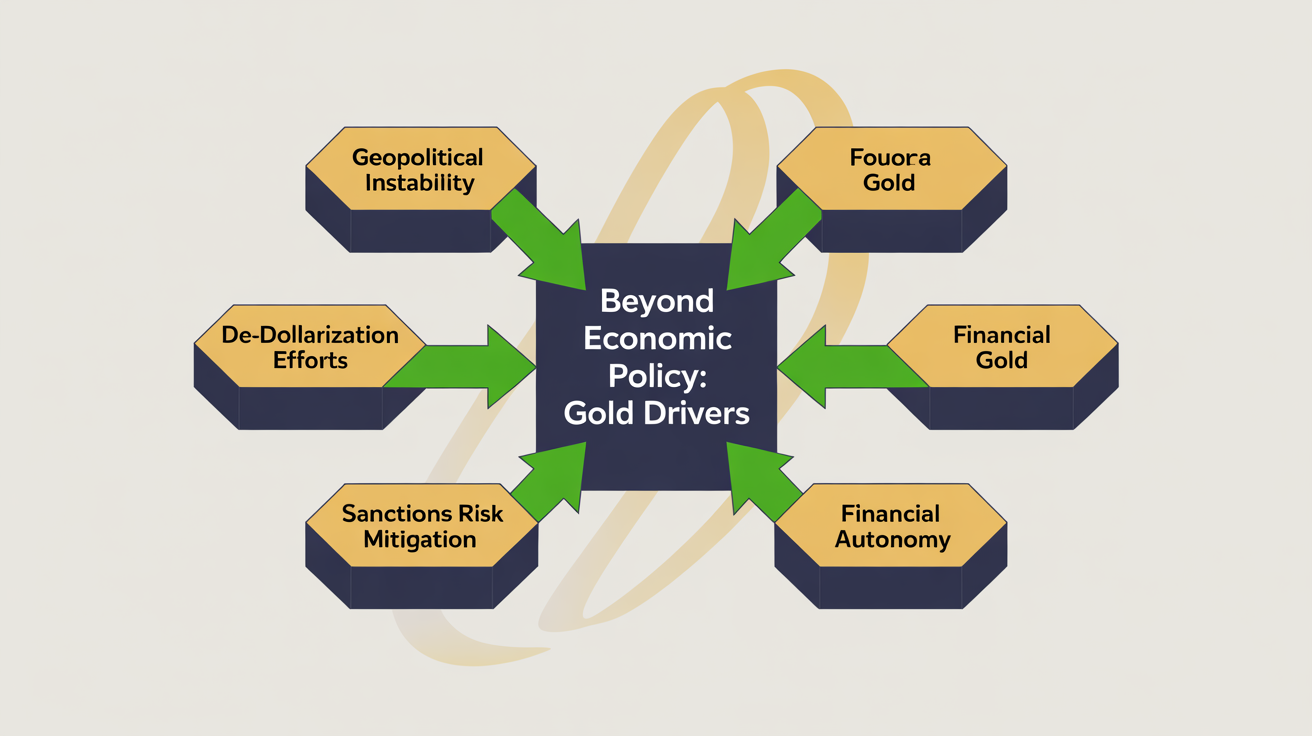
Beyond traditional economic factors, a significant and often overlooked driver of central bank gold accumulation is geopolitical instability and the desire for greater financial autonomy. This trend is particularly evident among emerging market central banks, who are strategically increasing their gold reserves as a hedge against US dollar hegemony and potential sanctions risk. This marks a departure from purely monetary policy considerations, signaling a potential shift in the global financial order. Central banks in emerging economies accounted for over 80% of net gold purchases in recent years, with China, India, and Turkey being prominent buyers. This strategic accumulation is driven by a desire for de-dollarization, reducing reliance on the US dollar as the primary reserve currency for trade and finance. Nations within the BRICS Nations bloc, for instance, are actively exploring alternative financial systems and increasing their gold holdings to bolster their economic independence. Unlike most guides, we delve into how the growing trend of de-dollarization by central banks is fundamentally reshaping the future demand for gold.
Should I invest in gold based on central bank actions?
Deciding whether to invest in gold based on central bank actions requires a nuanced understanding of their long-term strategies versus short-term market reactions. Central banks’ sustained buying trends indicate a fundamental confidence in gold as a strategic asset, providing a macro-level endorsement. However, individual investors must remember that central bank decisions are just one of many factors influencing gold prices, including interest rates, inflation, and overall market volatility. Interpreting central bank signals for gold investment involves monitoring key announcements, such as interest rate decisions from the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank. A hawkish stance (raising rates) generally pressures gold, while a dovish stance (lowering rates or implementing QE) tends to support it. While central bank actions provide valuable context, they should not be the sole determinant of an investment decision.
How can individual investors react to central bank policies on gold?
Individual investors can react to central bank policies on gold by adopting strategies that align with their personal financial goals and risk tolerance. One effective approach is portfolio diversification, including gold as a component to hedge against inflation and market volatility stemming from economic uncertainty. Dollar-cost averaging into gold investments can mitigate the impact of short-term price fluctuations. For those seeking exposure to gold, various investment vehicles are available, including physical gold (bullion, coins), gold ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds), and mining stocks. While speculative trading based on daily central bank news can be risky, a long-term holding strategy, viewing gold as a store of value and a hedge, often proves more resilient.
Turn Knowledge into Profit
You've done the reading, now it's time to act. The best way to learn is by doing. Open a free, no-risk demo account and practice your strategy with virtual funds today.
Open a Free Demo AccountWhere can I track central bank gold purchases?
Individual investors can track central bank gold purchases through several reputable sources. The World Gold Council is a leading authority, publishing quarterly reports on gold demand trends, which include detailed statistics on official sector demand. These reports provide insights into which central banks are actively buying or selling gold. Financial news outlets and specialized commodity research firms also frequently report on central bank activities.
Bottom Line
Central banks are pivotal in shaping global gold prices, acting through monetary policy, reserve management, and strategic responses to economic and geopolitical shifts. Their decisions on interest rates, quantitative easing, and gold purchases directly influence gold’s appeal as a safe haven and inflation hedge. Understanding these complex dynamics is essential for investors seeking to navigate the gold market effectively.
Key Takeaways
- Central banks influence gold prices through monetary policy, interest rates, and quantitative easing.
- Gold serves as a strategic reserve asset, offering diversification and a hedge against inflation and currency devaluation.
- Geopolitical instability and de-dollarization efforts are increasingly driving central bank gold accumulation.
- While central bank actions provide macro signals, individual investors must align gold investments with personal goals and risk tolerance.






