Bollinger Bands are a technical analysis tool designed to solve this problem by providing a clear framework for understanding market volatility and identifying potential trading opportunities. Think of them as a dynamic “river” for price action—they show you when the current is calm and when it’s raging.
While understanding Bollinger Bands is important, applying that knowledge is where the real growth happens. Create Your Free Forex Trading Account to practice with a free demo account and put your strategy to the test.
Key Takeaways
- Bollinger Bands measure market volatility, with the bands widening in high volatility and tightening (“squeezing”) in low volatility.
- A “squeeze,” when the bands contract, signals low volatility and often precedes a large price breakout in either direction.
- The price touching the upper band suggests a potential overbought condition, while touching the lower band suggests a potential oversold condition.
- Never treat a band touch as an automatic buy or sell signal; it is a signal to investigate, not a command to trade.
- Always confirm Bollinger Band signals with another indicator, like using the RSI to validate overbought or oversold conditions.
- Bollinger Bands are a lagging indicator; they provide context about current market conditions, not predict future prices.
What are Bollinger Bands?
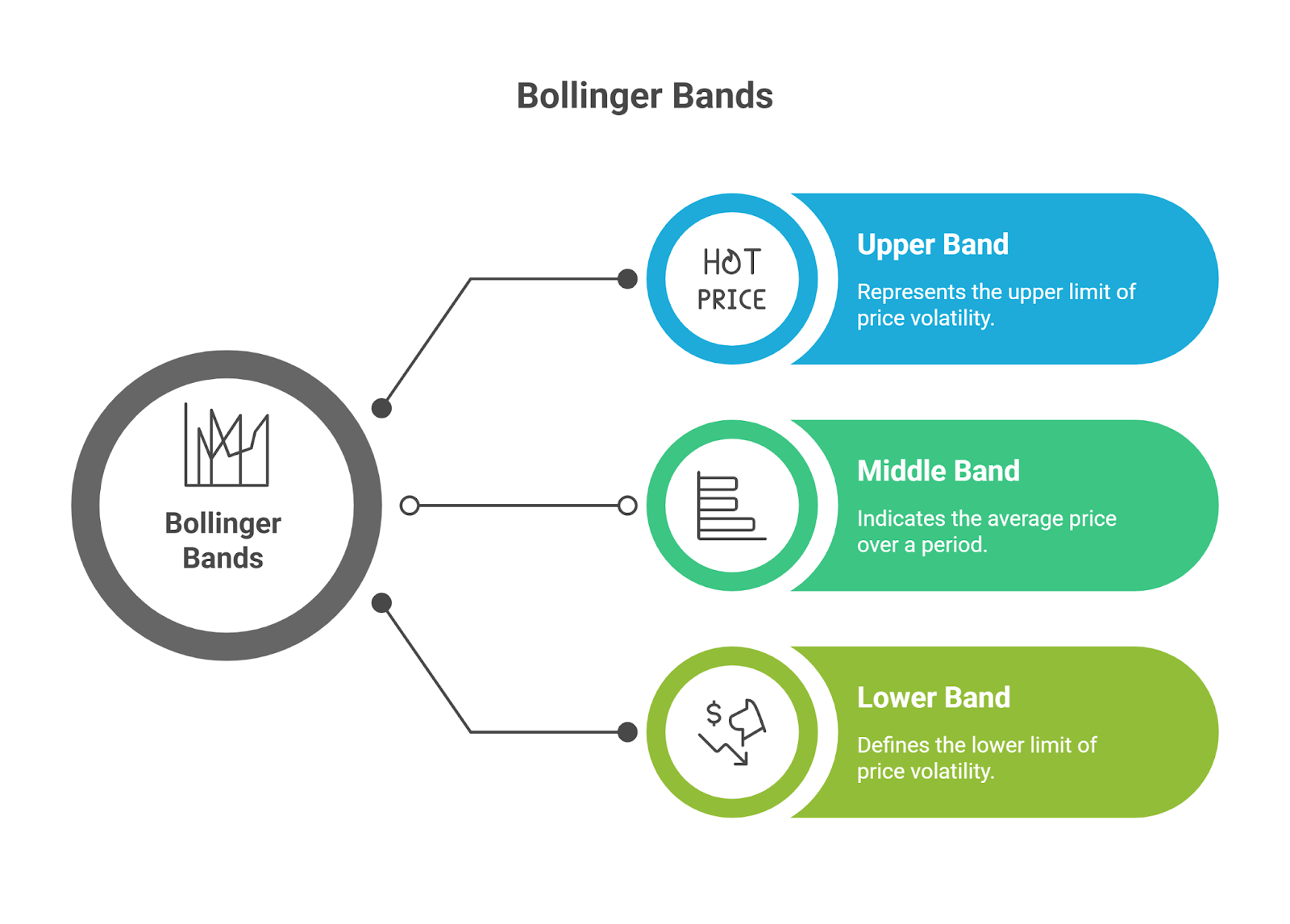
Bollinger Bands are three lines drawn on a trading chart that measure market volatility and provide a relative definition of high and low prices. They create a dynamic channel that contains the majority of an asset’s price action.
Who created Bollinger Bands?
The indicator was developed in the early 1980s by John Bollinger, a highly respected American technical analyst and money manager. His goal was to create an adaptive trading tool that could respond to changing market conditions, and it has since become one of the most widely used indicators in financial markets.
How are the bands calculated?
The bands are statistically derived from recent price action. While the math can be complex, the construction is straightforward:
- Middle Band: A 20-period simple moving average (SMA).
- Upper Band: The Middle Band + (2 x 20-day standard deviation).
- Lower Band: The Middle Band – (2 x 20-day standard deviation).
How do Bollinger Bands measure market volatility?
Bollinger Bands measure volatility through their width, as the distance between the upper and lower bands directly reflects how much prices are fluctuating.
- Band Expansion (High Volatility): When the market is volatile and prices are making large swings, the bands widen or expand. This signals that significant price movement is occurring.
- Band Contraction (The “Squeeze”): When the market is calm and prices are stable, the bands narrow or contract. A squeeze indicates low volatility and often precedes a significant price breakout, like a coiled spring ready to release. Breakout confirmation improves if the squeeze aligns with volume divergence in Forex, since rising volume validates the move.
Ready to Elevate Your Trading?
You have the information. Now, get the platform. Join thousands of successful traders who use Volity for its powerful tools, fast execution, and dedicated support.
Create Your Account in Under 3 MinutesHow to Read Price Action with Bollinger Bands?
It’s crucial to backtest price action analysis with Bollinger Bands on historical data. Start with smaller position sizes and gradually refine your strategy based on observed patterns.
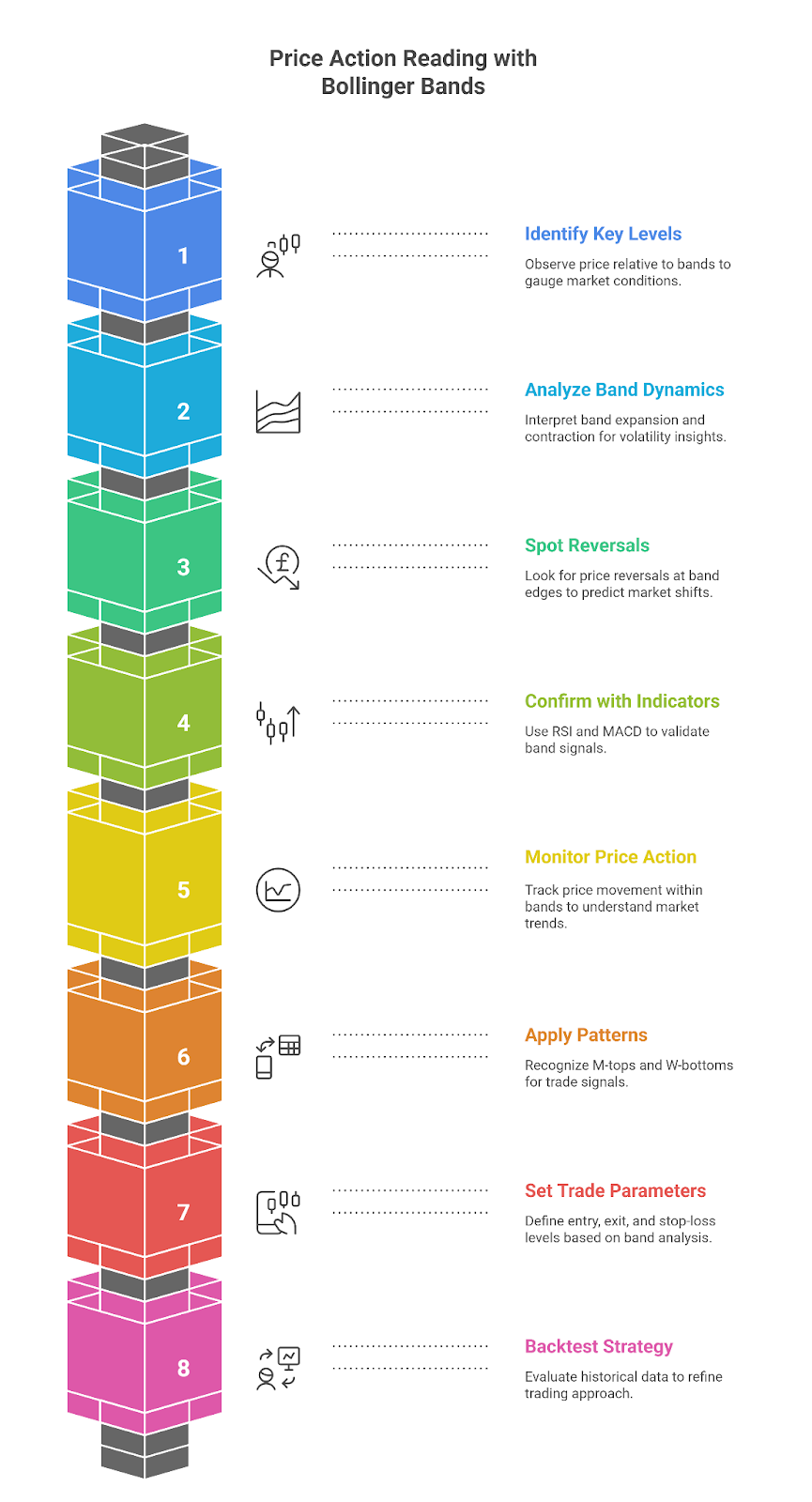
Step 1: Identify Key Levels on the Chart
- Examine the Bands: Observe the position of the price relative to the upper, middle, and lower bands.
- Upper Band indicates potential overbought conditions.
- Lower Band indicates potential oversold conditions.
- Middle Band reflects the 20-period moving average, serving as a trend indicator.
For instance, if the price is consistently near the upper band during an uptrend, the market likely has strong bullish momentum.
Step 2: Analyze Band Expansion and Contraction
- Band Contraction (Squeeze): Signals low volatility and precedes a potential breakout.
- Band Expansion: Indicates increased volatility and supports ongoing trends.
For example, in September 2024, EUR/USD showed a band squeeze before a breakout, which moved prices 50 pips higher within two days.
Step 3: Look for Reversals at Key Levels
- Upper Band Reversal: If the price touches or breaches the upper band but fails to maintain momentum, it could indicate a reversal.
- Lower Band Reversal: Similar behavior near the lower band signals potential bullish reversals.
- Confirm reversals with patterns like M-tops (bearish) or W-bottoms (bullish). These setups are often treated as Bollinger band signals, especially when combined with classic reversal structures.
For example, GBP/USD in January 2024 formed a W-bottom, where the price rebounded after failing to break below the lower band.
Step 4: Combine Indicators for Confirmation
- Add RSI: Use RSI Indicator to confirm overbought (above 70) or oversold (below 30) conditions near the bands.
- Use MACD: Validate breakout signals during squeezes with MACD crossovers.
For example, in March 2024, USD/JPY showed RSI above 70 as the price approached the upper band, which confirmed overbought conditions.
Step 5: Monitor Price Action within the Bands
- Trending Markets: Prices moving along the upper band indicate bullish strength; lower bands show bearish momentum.
- Range-Bound Markets: Look for oscillations between the upper and lower bands to trade reversals.
Step 6: Apply Patterns for Entry and Exit Points
- Identify price patterns within Bollinger Bands:
- M-Tops: Bearish reversal signals.
- W-Bottoms: Bullish reversal signals.
Step 7: Set Your Trade Parameters
- Use the middle band as a target for counter-trend trades or the opposite band for trend-following strategies.
- Place stop-loss orders slightly outside the bands to minimize risks
For example, if entering a short trade on an M-top, set the stop-loss slightly above the upper band.
Step 8: Backtest and Refine Your Strategy
- Review historical data to see how Bollinger Bands would have performed with your trade setups.
- Adjust settings like band width and time frames to suit your trading style.
These patterns and behaviors provide the foundation for interpreting market volatility using Bollinger Bands. Now, let’s explore how to apply this knowledge in actionable trading strategies.
What are the most common Bollinger Band trading strategies?
The most common strategies involve using the bands to trade breakouts, follow trends, or identify reversals.
- The Squeeze (Breakout Trading): After the bands contract into a tight squeeze, wait for a price candle to close decisively outside one of the bands. This signals a volatility breakout, and you can trade in that direction.
- The Trend Follow: In a strong, established trend, use the middle band (20-period SMA) as an entry point. For example, in an uptrend, you could buy when the price pulls back to touch the middle band.
- The Reversal (Mean Reversion): In a sideways or range-bound market, prices tend to bounce between the outer bands. You can sell when the price hits the upper band and buy when it hits the lower band, with the middle band as a potential profit target.
How can you combine Bollinger Bands with other indicators?
You can enhance signal accuracy by combining Bollinger Bands with other indicators that provide confirmation for momentum and trend.
- With the Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI can confirm overbought or oversold conditions. If the price hits the upper Bollinger Band and the RSI is above 70 (overbought), the signal for a potential sell-off is much stronger.
- With the MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): The MACD Indicator is great for confirming breakouts from a Bollinger Band squeeze. If the bands are squeezing and the price breaks out upward, a bullish crossover on the MACD can confirm that the new uptrend has momentum. Some traders also use Ichimoku + Bollinger Bands together, where Ichimoku defines trend structure while Bollinger squeezes confirm breakout pressure.
What are the limitations of Bollinger Bands?
While powerful, Bollinger Bands are not foolproof and come with key limitations that every trader must understand. Recognizing these weaknesses is essential for using the tool responsibly.
- They are a lagging indicator: Because the bands are calculated using a simple moving average, they are inherently reactive to past price data. They don’t predict the future; they provide context for the present.
- They don’t predict direction: A Bollinger Band squeeze correctly signals that volatility is about to increase, but it gives no information about whether the resulting breakout will be up or down.
- They can produce false signals: In a choppy, sideways market with no clear trend, the price can cross back and forth over the bands frequently, generating many misleading overbought and oversold signals.
Risk Management Using Bollinger Bands
- Set stop-loss orders below the lower band in bullish trades or above the upper band in bearish trades.
- Adjust position size based on the width of the Bollinger Bands to reflect market volatility.
- Exit trades when the price touches the opposite band to lock in profits during trending conditions.
- Avoid trading during narrow band squeezes without confirmation indicators to prevent false breakouts.
- Use the middle band as a dynamic trailing stop to follow the trend and protect gains.
- Combine Bollinger Bands with risk metrics like ATR to calculate appropriate position sizes.
- Avoid overleveraging by aligning trade size with the current band width and overall volatility.
- Diversify trades across instruments to reduce risk exposure from a single market.
- Rely on confirmation from indicators like RSI or MACD before entering trades at the bands.
- Regularly review trades to adjust strategies based on evolving volatility patterns.
Turn Knowledge into Profit
You've done the reading, now it's time to act. The best way to learn is by doing. Open a free, no-risk demo account and practice your strategy with virtual funds today.
Open a Free Demo AccountBottom Line
Bollinger Bands are not a standalone trading system but rather a powerful tool for providing context about market volatility. They help you understand whether the market is quiet or loud, trending or ranging.
By using them to identify squeezes, breakouts, and potential reversal points—and always confirming those signals with another indicator like RSI or MACD—you can turn them into a powerful part of your trading toolkit. Remember to always use proper risk management, like setting stop-loss orders, to protect your capital.






