Learn to trade gold with this comprehensive guide covering XAU/USD, CFDs, futures, ETFs, proven strategies, and essential risk management. This resource will help you understand market dynamics and develop a disciplined approach to gold trading.
What is Gold Trading?
Gold trading involves speculating on the price movements of gold rather than owning the physical metal itself. Traders aim to profit from price fluctuations by buying low and selling high—or by shorting when they expect prices to fall.
As one of the most actively traded precious metals, gold has historically been considered a potential safe haven during periods of market stress or geopolitical uncertainty. Its price is influenced by factors such as inflation, interest rates, central bank policy, and movements in the US dollar, which often shows an inverse correlation.
The currency code for gold spot is XAU, which refers to the price of one Troy ounce of gold. The XAU/USD currency pair represents this price against the US Dollar, making it the most liquid way to trade gold on forex markets.
Why Trade Gold?
Trading gold attracts investors for several compelling reasons:
- Portfolio diversification: Gold has historically shown low correlation with equity markets. During periods of economic stress or inflationary pressure, gold can behave differently from shares or indices, potentially making it attractive for hedging strategies.
- Inflation hedge: Gold often preserves purchasing power when traditional currencies devalue, making it a popular choice during periods of rising inflation.
- Safe-haven appeal: During economic or geopolitical instability, capital frequently flows into gold as investors seek stability.
- Market flexibility: With CFD trading, you can go long when expecting prices to rise or short when anticipating a decline—without needing to own or store physical metal.
- High liquidity: Gold markets operate nearly 24 hours on weekdays, supporting efficient execution and competitive spreads.
How Does Gold Trading Work?
Gold trading works by allowing investors to take positions on the future price direction of gold without physically holding the metal. Here’s how the key mechanics operate:

Buy and Sell Positions
As a gold trader, you might take a long position when you expect prices to rise, or go short if you think prices will fall. This flexibility means you can respond to a range of market conditions—from central bank policy shifts to geopolitical events—without taking delivery of the metal.
Spreads and Trading Costs
Gold CFD trading costs are typically reflected in the spread—the difference between the buy and sell price. Commissions or overnight charges may also apply. If you keep a position open beyond the trading day, overnight funding charges (also called swap fees) will accrue.
Trading on Margin
Gold CFDs are traded on margin, meaning you only need to deposit a percentage of the full trade value to open a position. This allows for greater exposure than your initial outlay, which can magnify both profits and losses.
Market Access
You can trade gold online through trading platforms available on desktop and mobile. High liquidity in gold markets supports efficient execution, although slippage may still occur during periods of heightened volatility.
What Are the Different Ways to Trade Gold?
Traders can access the gold market through several distinct financial instruments, each offering different levels of leverage, cost, and exposure.
Gold CFDs (Contracts for Difference)
Gold CFDs allow speculation on price movements without owning the underlying asset. When trading a CFD, you enter into a contract with a broker to exchange the difference in gold’s price from when the contract opens until it closes.
Advantages:
- High leverage available
- No physical storage required
- Can profit from both rising and falling markets
- Flexible position sizes
Considerations:
- Overnight funding charges apply
- Leverage amplifies both gains and losses
- Requires active risk management
Gold Futures Contracts
Gold futures are standardized, legally binding agreements to buy or sell a specific quantity of gold at a predetermined price on a future date. Unlike CFDs, futures are exchange-traded through venues like COMEX (part of CME Group).
Advantages:
- Transparent, exchange-traded pricing
- Used for hedging and price discovery
- Direct exposure to commodity price
Considerations:
- Larger contract sizes (typically 100 oz for standard contracts)
- Fixed expiration dates
- Higher capital requirements
- More suitable for institutional traders
Gold ETFs (Exchange-Traded Funds)
Gold ETFs offer a simpler, less leveraged way to gain exposure to gold prices. These investment funds trade on stock exchanges like regular shares and typically hold physical gold or gold-related derivatives.
Advantages:
- Lower volatility than CFDs or futures
- No margin calls
- Easy to buy and sell through standard brokerage accounts
- Suitable for long-term investment
Considerations:
- Management fees reduce returns
- Less flexibility for short-term trading
- Lower potential returns due to lack of leverage
Gold Spot vs. Gold Futures CFDs
Gold spot CFDs reflect the live market price of gold, typically quoted for immediate settlement. This is the most common benchmark for gold CFDs, giving you exposure to short-term price moves.
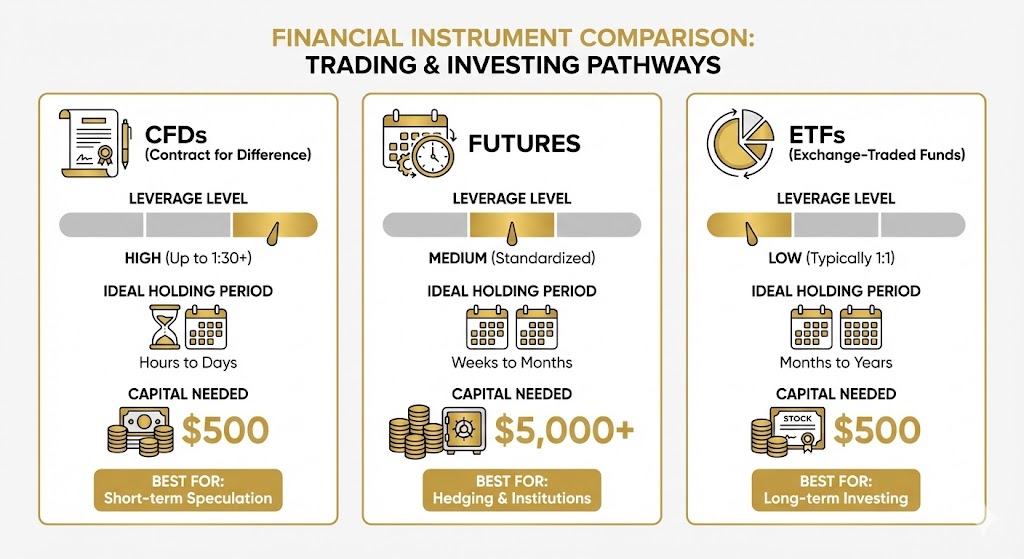
Gold futures CFDs track the price movements of gold futures contracts. Futures prices often trade at a premium or discount to spot, depending on market sentiment, interest rates, and time to expiry.
| Feature | Gold CFDs | Gold Futures | Gold ETFs |
| Ownership | No physical gold | No physical gold | Indirect (fund holds gold) |
| Leverage | High | Moderate to High | Low (equity-like) |
| Market | OTC (broker network) | Centralized exchange | Stock exchange |
| Contract Size | Flexible | Standardized (100 oz) | Share-based |
| Expiration | No (continuous) | Yes (fixed date) | No (like stocks) |
| Margin Calls | Yes | Yes | No |
| Cost Structure | Spreads + overnight fees | Commissions + exchange fees | Management fees |
| Ideal For | Short-term speculation | Hedging/institutional | Long-term investment |
Gold Market Trading Hours
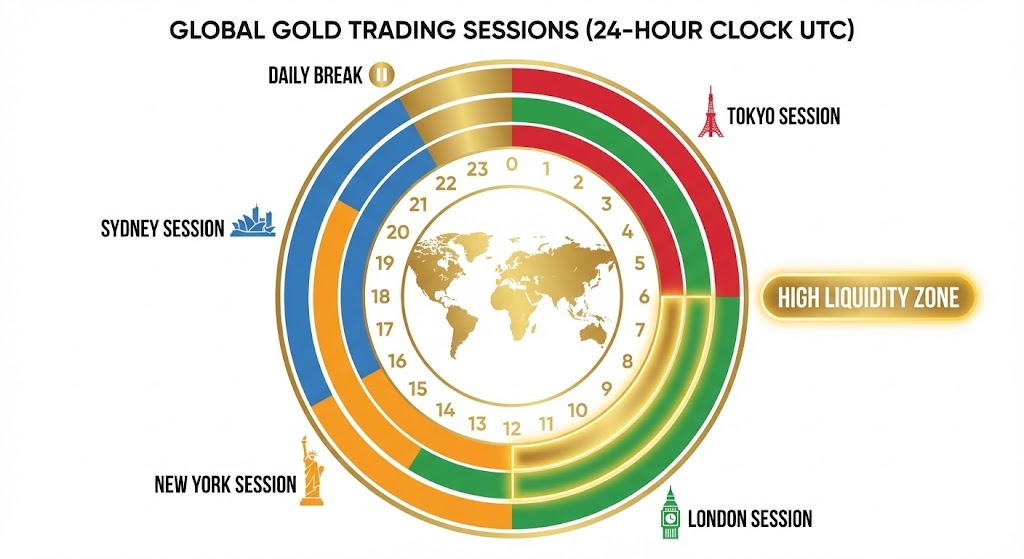
As a globally traded commodity, gold trading hours run nearly around the clock during weekdays.
| Market | Summer Hours (UTC) | Winter Hours (UTC) | Daily Break (UTC) |
| Gold Spot | Sunday 10:00 pm – Friday 9:00 pm | Sunday 11:00 pm – Friday 10:00 pm | 9:00 pm – 10:00 pm |
| Gold Futures | Sunday 10:00 pm – Friday 9:00 pm | Sunday 11:00 pm – Friday 10:00 pm | 10:00 pm – 11:00 pm |
Best times to trade: The overlap of major trading sessions—particularly London and New York (1pm–5pm UTC in summer)—typically sees increased liquidity and volatility, offering more trading opportunities.
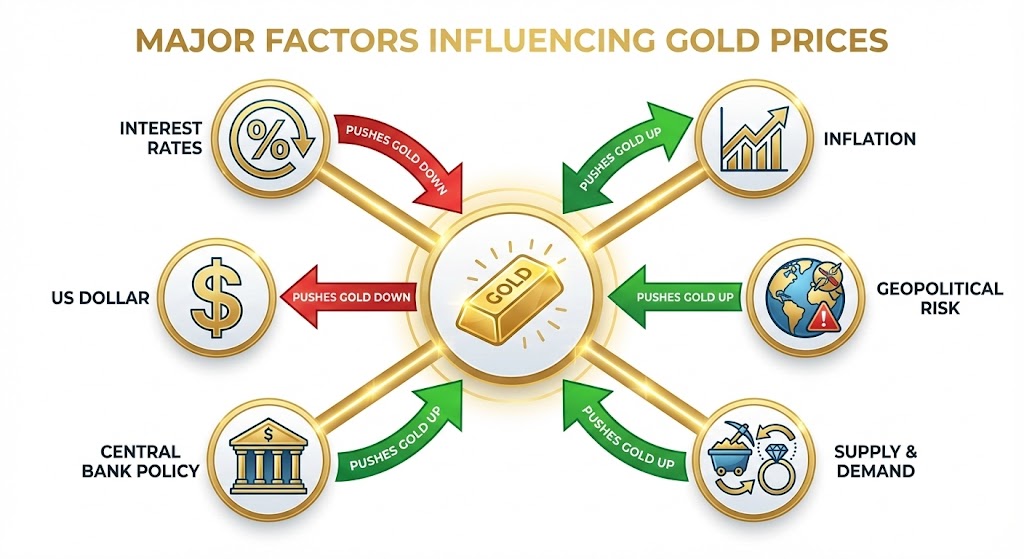
What Factors Affect Gold Prices?
Understanding what moves gold prices is essential for developing effective trading strategies.
Economic Indicators
- Inflation: Higher inflation can boost gold’s appeal as a hedge against currency devaluation. When inflation expectations rise, gold often strengthens.
- Interest rates: Rising interest rates can make bonds and other fixed-income investments more attractive relative to non-yielding gold, potentially reducing demand. Conversely, lower rates tend to support gold prices.
- Economic data releases: Reports like US non-farm payrolls, GDP figures, and inflation data can cause sharp short-term price movements.
US Dollar Strength
Gold is priced in US dollars globally. A stronger dollar makes gold more expensive for holders of other currencies, potentially dampening international demand. A weaker dollar has the opposite effect.
Geopolitical Events
Wars, political instability, international tensions, and other geopolitical risks often increase demand for gold as investors seek safety.
Central Bank Policy
Central bank decisions regarding interest rates, quantitative easing, and monetary policy significantly impact gold prices. Dovish policy (lower rates, more stimulus) typically supports gold; hawkish policy (higher rates, tightening) can pressure it.
Supply and Demand
Physical gold supply from mining operations and demand from jewelry, technology, and investment sectors influence longer-term price trends.
Why Has Gold Risen Since 2023?
Several factors have contributed to gold’s appreciation:
- Persistent inflation concerns driving hedging demand
- Geopolitical tensions increasing safe-haven flows
- Central bank gold purchases, particularly from emerging markets
- Periods of US dollar weakness
What Could Push Gold Lower?
- Sustained higher interest rates making bonds more attractive
- A significantly stronger US dollar
- Reduced geopolitical tensions
- Lower inflation expectations
- Risk-on sentiment drawing capital toward equities
Gold Trading Strategies
Which gold trading strategy suits you best depends on your timeframe, risk tolerance, and available time for market analysis.
Day Trading
Day traders open and close multiple positions within the same trading day, aiming to capitalize on intraday volatility.
How it works with gold:
- Monitor key economic data releases (US inflation, non-farm payrolls, Fed announcements)
- Use technical indicators like support/resistance levels, moving averages, and RSI
- Set tight stop-losses to manage rapid price movements
- Requires constant market monitoring
Best for: Traders with time to watch markets actively and quick decision-making ability.
Swing Trading
Swing trading involves holding positions for several days to a few weeks to capture medium-term price moves.
How it works with gold:
- Identify trends using daily and 4-hour charts
- Use tools like RSI, Fibonacci retracements, and candlestick patterns
- Look for entries at technical support/resistance levels
- Allow wider stop-losses than day trading
Best for: Traders who can’t monitor markets constantly but want more active involvement than long-term investing.
Trend Trading
Trend traders aim to follow sustained moves in gold’s price—either upward or downward.
How it works with gold:
- Use moving averages (50-day, 200-day) to identify trend direction
- Apply trendlines and the ADX indicator to assess trend strength
- Hold positions as long as the trend remains intact
- Accept that you won’t catch exact tops or bottoms
Best for: Traders comfortable with longer holding periods who want to capture major moves.
Position Trading
Position trading is a longer-term approach where traders hold positions for weeks or months.
How it works with gold:
- Base decisions on macroeconomic factors: central bank policy, inflation expectations, geopolitical risk
- Use wider stop-losses to accommodate normal volatility
- Monitor margin requirements carefully for leveraged positions
- Focus on fundamental analysis over technical signals
Best for: Traders with a longer time horizon and patience for positions to develop.
News Trading
News trading focuses on capitalizing on price movements following major announcements.
How it works with gold:
- Track economic calendar for high-impact events
- Position before or immediately after announcements
- Be prepared for high volatility and potential slippage
- Use appropriate position sizing given increased risk
Best for: Experienced traders comfortable with fast-moving markets.
Analyzing Gold Market Trends
Successful trading combines both approaches:
Technical analysis focuses on past price data and chart patterns. Key tools include:
- Moving averages (identifying trend direction)
- RSI (measuring overbought/oversold conditions)
- Fibonacci retracements (finding potential reversal levels)
- Support and resistance levels (identifying entry/exit points)
Fundamental analysis examines economic, financial, and geopolitical factors:
- Interest rate expectations
- Inflation data and forecasts
- US dollar index movements
- Central bank statements and policy decisions
- Geopolitical developments
Risk Management for Gold Trading
Effective risk management is what separates successful traders from those who blow their accounts. Gold’s volatility makes this especially important.
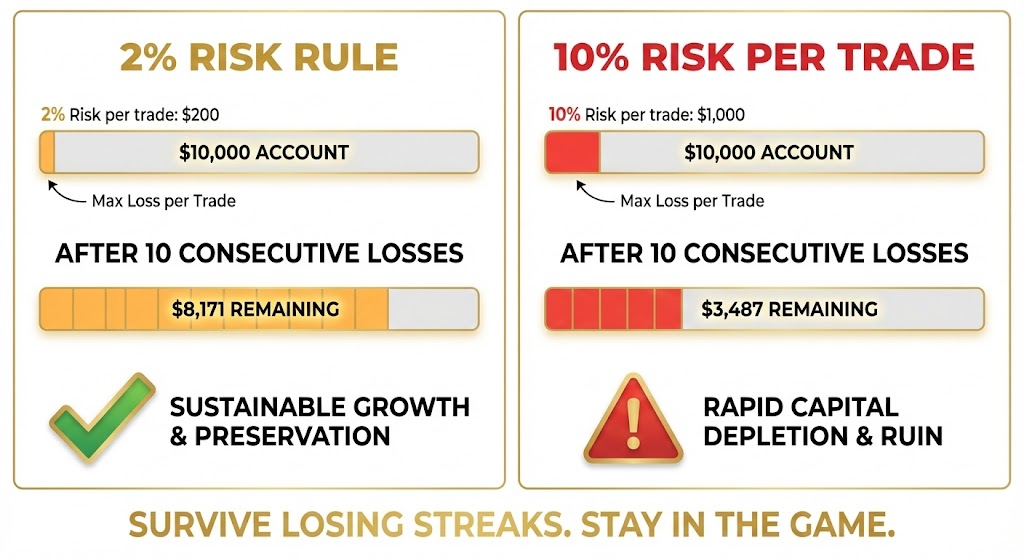
The 1-2% Rule
A foundational principle: never risk more than 1-2% of your total trading capital on any single trade.
This means if you have a $10,000 account, your maximum loss on any trade should be $100-$200. This approach ensures no single loss can severely impact your overall account.
Stop-Loss Orders
A stop-loss order automatically closes your trade when the price reaches a predetermined level, limiting potential losses.
How to set effective stop-losses:
- Place below recent support (for long positions) or above resistance (for shorts)
- Account for normal market volatility—too tight and you’ll get stopped out by noise
- Never move stop-losses further away to “give the trade room”
Position Sizing
Position sizing determines how many units or lots to trade based on your account size and acceptable risk per trade.
Formula:
Position Size = (Account Risk Amount) ÷ (Stop-Loss Distance in Points × Point Value)
Leverage: A Double-Edged Sword
While leverage can amplify returns, it equally magnifies losses.
Recommended leverage for beginners: Start with lower ratios (1:10 to 1:50) to limit potential downside while learning.
High leverage risks:
- Rapid account depletion from minor market fluctuations
- Margin calls requiring additional funds
- Automatic position closure at losses
Risk/Reward Scenarios
This table illustrates how stop-loss and position sizing work together:
| Account Size | Risk per Trade (2%) | Stop-Loss (points) | Position Size | Entry | Stop-Loss | Target (2:1 R:R) | Potential Profit | Potential Loss |
| $5,000 | $100 | 20 | £5/point | $2,300 | $2,280 | $2,340 | $200 | $100 |
| $10,000 | $200 | 20 | £10/point | $2,300 | $2,280 | $2,340 | $400 | $200 |
| $10,000 | $200 | 40 | £5/point | $2,300 | $2,260 | $2,380 | $400 | $200 |
| $25,000 | $500 | 25 | £20/point | $2,300 | $2,275 | $2,350 | $1,000 | $500 |
Practical Gold Trading Examples
Example 1: Long Position on Gold Spot CFD
Scenario: Gold is trading at $2,300 per ounce. After a lower-than-expected US inflation report, you expect the price to rise.
The trade:
- You open a long gold CFD at £10 per point
- This means you’ll make or lose £10 for every $1 movement in gold’s price
- With a 5% margin requirement, you deposit £1,150 to open the position (£10 × $2,300 × 5%)
Outcome A (Profitable):
- Gold rises to $2,320
- That’s a 20-point move in your favor
- You close the position for a gross profit of £200 (20 × £10), before spread and overnight costs
Outcome B (Loss):
- Gold drops to $2,280
- That’s a 20-point move against you
- You close the position for a loss of £200 (20 × £10), plus any applicable fees
Example 2: Short Position on Gold Futures CFD
Scenario: You expect gold prices to fall based on upcoming hawkish commentary from the US Federal Reserve.
The trade:
- Gold futures trade at $2,320
- You go short at £10 per point
- With 5% margin, you deposit £1,160
Outcome A (Profitable):
- Gold falls to $2,300
- You close for a 20-point gain: £200 profit (before costs)
Outcome B (Loss):
- Gold rises to $2,340
- That same 20-point move results in a £200 loss, excluding spread
Example 3: Position Sizing in Practice
Scenario: You have a $10,000 account and want to trade gold at $2,300 with a 25-point stop-loss, risking 2% of your account.
Calculation:
- Maximum risk: $10,000 × 2% = $200
- Stop-loss distance: 25 points
- Position size: $200 ÷ 25 = $8 per point
If gold moves 25 points against you, you lose exactly $200 (2% of your account). If it moves 50 points in your favor (2:1 reward-to-risk), you gain $400.
Why Do Beginners Lose Money Trading Gold?
Understanding common pitfalls helps you avoid them.
Emotional Decision-Making
- FOMO (Fear of Missing Out): Jumping into trades without proper analysis because the market is moving.
- Revenge trading: Trying to immediately recover losses by taking larger, riskier positions.
- Greed: Moving take-profit targets further away or removing them entirely when trades go well.
- Fear: Closing profitable trades too early or moving stop-losses to avoid small losses.
Poor Risk Management
- Risking too much on single trades
- Not using stop-losses
- Over-leveraging positions
- Not understanding margin requirements
Lack of Strategy
- Trading without a clear plan
- Switching strategies after a few losses
- Not keeping a trading journal
- Ignoring the importance of risk-reward ratios
Strategies for a Disciplined Trading Mindset
- Develop and follow a trading plan: Define your entry criteria, exit strategies, and risk management rules before trading.
- Keep a trading journal: Record every trade, including your emotional state, reasoning, and outcome. Review regularly to identify patterns.
- Use predetermined position sizes: Calculate your position size based on your risk rules before entering, not during.
- Accept losses as part of trading: Even the best strategies have losing trades. Focus on executing your plan, not on individual trade outcomes.
- Step away when emotional: If you feel angry, anxious, or overly excited, close the charts and return when calm.
How to Choose a Gold Trading Platform?
Selecting the right platform is crucial for your trading experience.
Key Factors to Consider:
Regulation: Always choose a broker regulated by reputable authorities such as:
- FCA (Financial Conduct Authority, UK)
- ASIC (Australian Securities and Investments Commission)
- CySEC (Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission)
- NFA/CFTC (United States)
Costs: Compare:
- Spreads on gold instruments
- Commissions per trade
- Overnight financing charges
- Withdrawal fees
Instruments available: Ensure the platform offers the gold products you want to trade (spot CFDs, futures CFDs, ETFs).
Platform features:
- Charting tools and technical indicators
- Mobile app availability
- Order types (stop-loss, take-profit, trailing stops)
- Execution speed
Customer support: Responsive support is valuable, especially for beginners.
What is the Minimum Capital to Trade Gold?
Minimum requirements vary by broker and instrument:
| Trading Type | Typical Minimum | Recommended Starting Capital |
| Gold CFDs (micro lots) | $50-$100 | $500-$1,000 |
| Gold CFDs (standard) | $500-$1,000 | $2,000-$5,000 |
| Gold Futures | $5,000-$10,000 | $25,000+ |
| Gold ETFs | Price of one share | $500-$1,000 |
How to Open a Gold Trading Account?
- Research and select a regulated broker that meets your needs
- Complete the online application with personal and financial information
- Verify your identity by submitting required documents (ID, proof of address)
- Fund your account via bank transfer, card, or e-wallet
- Familiarize yourself with the platform using demo mode if available
- Start trading with proper risk management in place
Where Can You Trade Gold?
Gold trading is available through derivatives markets accessed via regulated online brokers. Key venues that underpin gold CFD and futures pricing include:
- Volity.io: A secure, multi-asset trading platform that lets traders trade gold alongside forex and crypto, operating through its partnership with CySEC-regulated UBK Markets. It offers tight spreads on XAU/USD and XAU/EUR, MetaTrader 4/5 and a proprietary platform, volume-based cashback, swap-free accounts, and a high-performance mobile app—making it a comprehensive online gold trading solution.
- COMEX (CME Group): A major exchange for gold futures, widely used as a reference point for gold derivatives pricing.
- London OTC Gold Market: The primary global venue for physical gold trading. The London Bullion Market Association (LBMA) administers the LBMA Gold Price, a benchmark often referenced in gold spot CFD pricing.
- Shanghai Gold Exchange (SGE): A leading physical gold trading hub in Asia that contributes to regional and global price discovery through the Shanghai Gold Price benchmark.
Key Takeaways
- Gold’s price is influenced by inflation, interest rates, the US dollar, and geopolitical events.
- Choose your trading instrument (CFDs, futures, or ETFs) based on your goals and risk tolerance.
- Never risk more than 1-2% of your capital on any single trade.
- Always use stop-losses and proper position sizing.
- Develop a trading plan and stick to it, especially during emotional moments.
- Start with lower leverage and increase only as you gain experience.
Conclusion
Gold trading offers opportunities to profit from one of the world’s most liquid and historically significant markets. Success requires understanding market dynamics, choosing appropriate instruments, implementing proven strategies, and—most critically—maintaining disciplined risk management.
Whether you’re looking for short-term trading opportunities or longer-term portfolio diversification, gold can be a valuable addition to your trading approach—provided you approach it with proper preparation and discipline.
Frequently Asked Questions
Disclaimer: Trading gold and other financial instruments carries significant risk. Past performance is not indicative of future results. This content is for educational purposes only and should not be considered financial advice. Always conduct your own research and consider consulting a qualified financial advisor before trading.






