The Crypto Ledger, a hardware wallet like the Ledger Nano X, is essential for securing digital assets by keeping private keys offline. It offers robust cold storage protection against cyber threats, ensuring true self-custody of your cryptocurrency. This guide explains how these devices work, their advanced security features, and how to set up and manage your funds safely. By reading this, you will be able to confidently protect your crypto from loss and scams.
What is a crypto ledger?
A crypto ledger is a hardware wallet that physically secures your cryptocurrency by isolating your private keys from online vulnerabilities. This specialized device acts as a robust cold storage solution, generating the digital signatures required to move your digital assets in an offline environment.
Unlike software wallets, a hardware wallet’s primary function is to provide an impenetrable barrier between your sensitive cryptographic information and potential cyber threats.
While understanding Ledger is important, applying that knowledge is where the real growth happens. Create Your Free Crypto Trading Account to practice with a free demo account and put your strategy to the test.
How does a crypto ledger work?
A hardware wallet, such as the Ledger Nano X, functions by storing your private keys offline, ensuring they are never exposed to the internet. When you initiate a transaction, the device uses its internal secure element chip to sign the transaction without revealing your private key to your computer or phone.
This signed transaction is then broadcast to the blockchain via your connected device, significantly reducing the risk of online theft. A hardware wallet, like the Ledger Nano X, is a form of cold storage, meaning private keys remain offline, which minimizes online theft risks.
What is the difference between a crypto ledger and a crypto wallet?
The terms “crypto ledger” and “crypto wallet” are often used interchangeably, but there’s a key distinction rooted in their form and security. A crypto wallet is a broader term, referring to any interface that allows you to manage your cryptocurrency, whether it’s software-based (hot wallet) or hardware-based (cold wallet).
A crypto ledger, specifically, refers to a hardware wallet—a physical device that provides the highest level of security by storing your private keys offline. Ledger hardware wallets are specifically designed to protect crypto assets from hackers by keeping private keys offline within a certified secure element chip.
Is a crypto ledger safe?
A crypto ledger is considered one of the safest methods for storing digital assets, primarily because it keeps your private keys offline, isolated from internet-connected devices. The fundamental principle is that your private keys, which represent true ownership of your cryptocurrency, are never exposed to online threats.
This offline nature is the cornerstone of its robust security, protecting against hacking, malware, and other cyberattacks.
How do private keys secure a crypto ledger?
Private keys are the cryptographic secret that proves ownership of your cryptocurrency on the blockchain. A hardware wallet secures these keys by generating and storing them within a dedicated, tamper-resistant chip, known as a secure element. This means the private keys never leave the device, even when connected to a computer, making them virtually inaccessible to malicious software or hackers. This private key ownership is paramount to self-custody wallet security.
What if I lose my seed phrase?
If you lose your seed phrase, also known as your recovery phrase, you risk permanently losing access to your digital assets. The seed phrase is a sequence of 12 or 24 words that acts as the master backup for all your private keys.
It is the only way to restore access to your cryptocurrency if your hardware wallet is lost, stolen, or damaged. Therefore, securely storing your 24-word recovery phrase offline, away from prying eyes, is critical for safeguarding your funds.
How do public addresses work with a crypto ledger?
A public address functions like a bank account number for your cryptocurrency, allowing you to receive digital assets. With a crypto ledger, you generate a public address through the device, often via the Ledger Live application. This address is safe to share with others for receiving funds.
Unlike private keys, which must remain secret, your public address is visible on the blockchain and poses no security risk.
How do I protect my Ledger device physically?
You protect your Ledger device physically through a combination of a PIN code and the device’s auto-lock features. A strong PIN code is required to access the device and authorize transactions, preventing unauthorized physical access to your private keys.
If the device is lost or stolen, an incorrect PIN entry will trigger an automatic reset, erasing the device’s data and protecting your digital assets. Your recovery phrase remains the ultimate backup for such scenarios.
Ready to Elevate Your Trading?
You have the information. Now, get the platform. Join thousands of successful traders who use Volity for its powerful tools, fast execution, and dedicated support.
Create Your Account in Under 3 MinutesWhat is Ledger Nano S/X?
The Ledger Nano X is a flagship hardware wallet offered by Ledger, designed to provide advanced security and convenience for managing a wide range of digital assets. It distinguishes itself with its multi-currency support and Bluetooth connectivity, allowing users to manage their cryptocurrency on the go via the Ledger Live application on mobile devices.
This device represents a significant leap in accessibility for hardware wallet users, combining robust cold storage solution with modern features.
Multi-Currency, Bluetooth-Enabled Guardian
The Ledger Nano X serves as a versatile, Bluetooth connectivity enabled hardware wallet capable of securing a vast array of cryptocurrencies. This device supports over 5,500 digital assets, including major ones like Bitcoin, Ethereum, and XRP, alongside a broad spectrum of ERC-20 tokens, as stated by Ledger.com.
Its USB Connection (USB-C) also provides reliable wired connectivity, offering flexibility for both desktop and mobile users. This makes it an excellent choice for those with diverse portfolios, including various altcoins.
What are the benefits of using a hardware wallet like Ledger?
Using a hardware wallet like Ledger offers multiple benefits, primarily centered on improved security and user control. These devices provide cold storage, keeping your private keys offline and safe from online threats such as malware and phishing scams. They enable true private key ownership, meaning you have full control over your digital assets.
The Ledger Nano X further adds convenience with its Bluetooth connectivity and broad digital assets support, making it a portable and versatile secure digital assets management tool.
How does Ledger Live improve the Ledger Nano X experience?
Ledger Live is the essential companion application for the Ledger Nano X, significantly improving the user experience by providing a comprehensive interface for managing digital assets. Through Ledger Live, users can easily check their portfolio balance, send and receive cryptocurrency, stake assets to earn rewards, and install firmware update for their device. This integration ensures a seamless and secure interaction with the web3 ecosystem, and makes transaction management straightforward.
Can I lose my crypto with a Ledger?
No, you cannot lose your crypto with a Ledger device itself, provided you have securely stored your recovery phrase. The cryptocurrency is not physically stored on the device; rather, the device holds the private keys that grant access to your funds on the blockchain.
If your Ledger device is lost, stolen, or damaged, your digital assets remain safe and accessible by using your 24-word recovery phrase to restore your wallet on a new Ledger device or compatible software wallet.
How do I transfer crypto to a Ledger?
Transferring crypto to a Ledger device is a straightforward process managed primarily through the Ledger Live application. First, open Ledger Live and select the cryptocurrency account you wish to fund. Next, generate a public address for that account on your Ledger device. Carefully copy this address.
Finally, send funds from your exchange or another wallet to this public address, ensuring to double-check the address for accuracy before confirming the transaction. This method emphasizes self-custody wallet security.
The Power of Your Recovery Phrase
The recovery phrase, also known as the seed phrase, is the ultimate safeguard against permanent loss of your digital assets. While your hardware wallet protects your private keys physically, the recovery phrase is the encrypted backup for those keys.
If your device is compromised, lost, or broken, your cryptocurrency can be fully restored using this 24-word recovery phrase on a new device. The security of your funds relies entirely on the secrecy and safekeeping of this phrase.
PIN Codes and Auto-Lock Features
PIN codes are a crucial first line of defense for physically securing your Ledger device. You set a unique PIN during the initial setup, which is required to unlock the device and confirm transactions. Ledger devices also incorporate auto-lock features, automatically locking after a period of inactivity to prevent unauthorized access. These physical security measures work in tandem with the secure element chip to protect your private keys from both remote and local threats.
How do I choose a crypto ledger?
Choosing a crypto ledger involves considering various factors such as features, connectivity, and the range of digital assets supported, tailored to your individual needs. The market offers several options, with Ledger Nano X and Ledger Nano S Plus being prominent choices from Ledger.
Your decision should align with how you plan to interact with your cryptocurrency, whether primarily mobile or desktop, and the diversity of your portfolio.
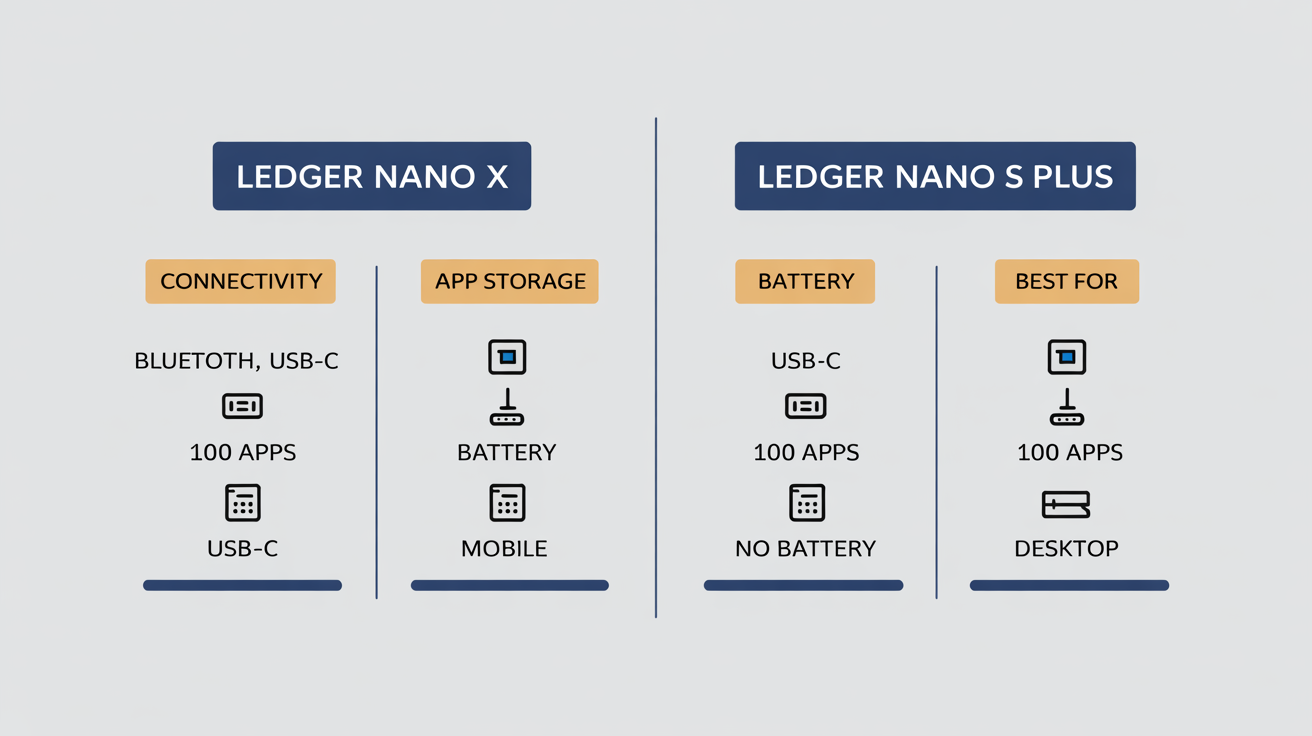
Comparing Ledger Nano X and Nano S Plus
The Ledger Nano X and Ledger Nano S Plus are both popular hardware wallets from Ledger, offering robust cold storage for digital assets. The Nano X is the premium model, featuring Bluetooth connectivity and a larger capacity for installing multiple cryptocurrency applications, supporting over 5,500 digital assets.
The Nano S Plus offers a more budget-friendly option with a USB Connection (USB-C) and slightly less app storage, but still provides the same core security and supports a wide range of assets.
| Connectivity | Bluetooth, USB-C | USB-C |
| App Storage | Up to 100 apps | Up to 100 apps |
| Supported Assets | 5,500+ digital assets | 5,500+ digital assets |
| Battery | Built-in battery (8 hrs) | No battery (USB powered) |
| Screen Size | Larger | Smaller |
| Price (Avg.) | ~$149 USD | ~$79 USD |
| Best For | Mobile users, large portfolios | Desktop users, budget-conscious |
The Ledger Nano X stands out with its Bluetooth connectivity, offering unparalleled convenience for mobile management of digital assets. The Ledger Nano S Plus, while lacking Bluetooth, provides an excellent entry point into hardware wallet security for desktop users.
Both devices ensure your private keys are protected by a secure element chip, upholding the highest standards of cold storage solution.
Advanced Security & Threat Mitigation
True crypto security extends beyond simply owning a hardware wallet; it requires understanding underlying technical protections and actively mitigating human-element vulnerabilities. While devices like the Ledger Nano X provide a strong foundation, users must also be aware of sophisticated attack vectors.
These include the specialized secure element chip technology, risks from supply chain attacks, and the pervasive threat of social engineering tactics.
What makes a Ledger hardware wallet uniquely secure?
A Ledger hardware wallet is uniquely secure due to its secure element chip, a tamper-resistant component similar to those found in passports and credit cards. This chip is certified with a CC EAL5+ certification, meaning it has undergone rigorous independent evaluation against advanced attack scenarios.
The secure element generates and stores your private keys in an isolated environment, making them impervious to software hacks and physical tampering, a core differentiator in hardware wallet security.
How do I know my Ledger device is genuine and safe?
To know if your Ledger device is genuine and safe, you must use the Ledger Live application’s Genuine Check feature. This feature verifies the authenticity of your device, confirming it is a legitimate Ledger product and has not been tampered with during transit.
This process is crucial for mitigating supply chain attacks, where malicious actors might try to intercept and compromise devices before they reach the customer. This Genuine Check feature confirms device authenticity and lack of tampering.
How can I avoid losing crypto to scams?
To avoid losing crypto to scams, you must be vigilant against social engineering tactics, which exploit human psychology rather than technical vulnerabilities. These scams often involve phishing emails, fake support accounts, or urgent demands for your seed phrase.
The critical rule is to never share your seed phrase or private keys with anyone, under any circumstances. Always verify the authenticity of websites and communications, and use strong, unique passwords for all your accounts to bolster your security.
How can I add an extra layer of security beyond my 24-word seed?
You can add an extra layer of security beyond your 24-word recovery phrase by using the passphrase feature, often referred to as the 25th word. This advanced feature allows you to create a separate, hidden wallet protected by a custom passphrase you choose.
If your main seed phrase is ever compromised or discovered under duress, you can truthfully provide it, but your primary digital assets would be hidden behind the additional passphrase, offering ultimate deniability and improved security.
How to set up a Ledger Nano X?
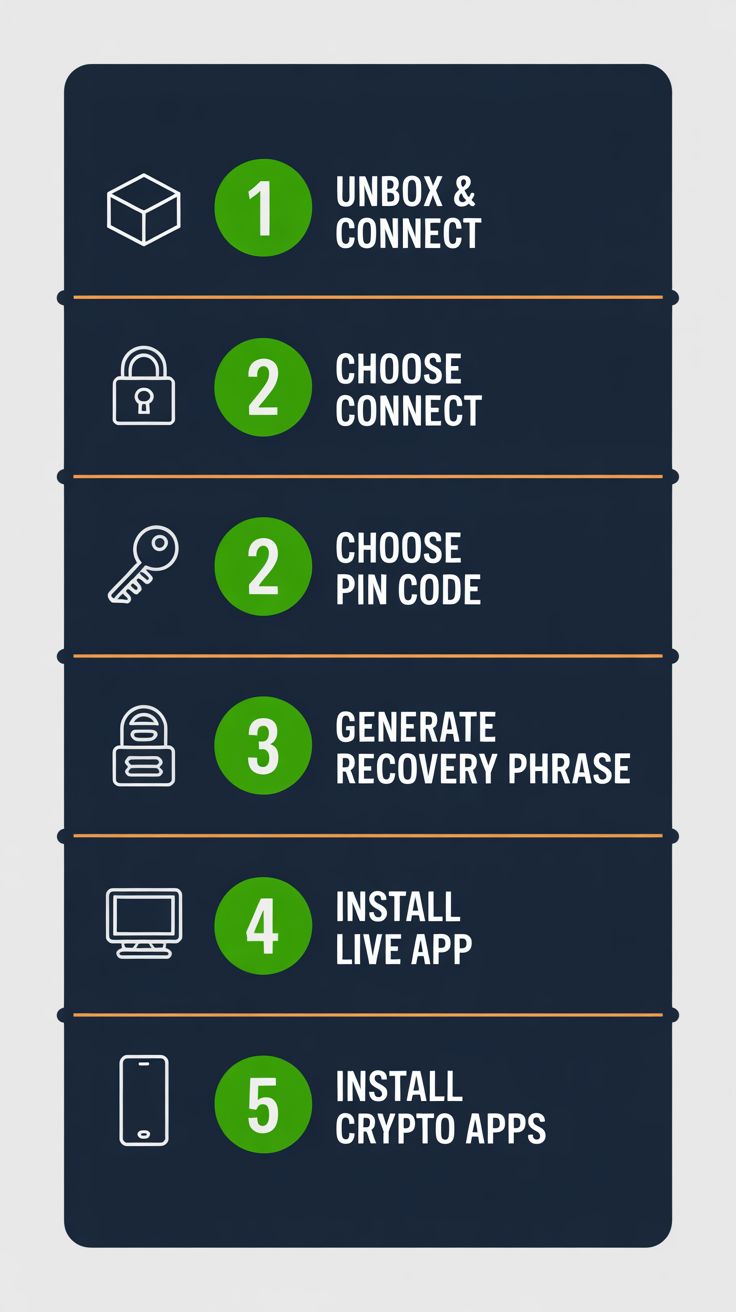
Setting up a Ledger Nano X involves a series of clear steps to initialize the device, secure your recovery phrase, and integrate with the Ledger Live application. This process ensures your private keys are generated and stored securely offline from the outset, establishing a robust cold storage solution for your digital assets.
Setting up a Ledger Nano X includes initializing the device, writing down a 24-word recovery phrase, and installing the Ledger Live application.
Initializing Your Ledger Nano X
Initializing your Ledger Nano X is straightforward:
- Unbox & Connect: Connect your new Ledger Nano X to your computer via the provided USB-C cable. The device will power on.
- Choose PIN: Follow the on-screen instructions to set a PIN code (4-8 digits). This PIN protects physical access to your device.
- Generate/Confirm Recovery Phrase: The device will display a 24-word recovery phrase. CRITICALLY, write these words down in the exact order on the provided recovery sheets. Never store this phrase digitally. The device will then ask you to confirm a few words to make sure you’ve recorded it correctly.
- Install Ledger Live: Download and install the Ledger Live application on your computer or mobile device.
- Install Apps on Device: Use Ledger Live to install the cryptocurrency applications (e.g., Bitcoin, Ethereum) onto your Ledger Nano X for the digital assets you wish to manage.
This process ensures your private keys are generated offline and backed up by your recovery phrase, establishing a highly secure self-custody wallet.
Turn Knowledge into Profit
You've done the reading, now it's time to act. The best way to learn is by doing. Open a free, no-risk demo account and practice your strategy with virtual funds today.
Open a Free Demo AccountWhere can I buy a Ledger Nano X?
You can buy a Ledger Nano X from authorized retailers to ensure you receive a genuine product and avoid potential supply chain attacks. The most reliable sources are the official Ledger website and major online retailers that are verified partners.
Purchasing directly from these trusted channels is crucial for the security of your digital assets.
Ensuring Authenticity
To ensure you receive an authentic Ledger Nano X and minimize the risk of a supply chain attack, purchase only from Ledger.com or its authorized resellers. Reputable platforms include Amazon.com and BestBuy.com.
Avoiding unofficial sellers or second-hand devices is paramount, as compromised devices could expose your private keys and digital assets to theft. Always use the Ledger Live application’s Genuine Check feature upon receipt.
How much does a Ledger Nano X cost?
The average price for a Ledger Nano X is approximately $149 USD, though prices can vary based on retailers and ongoing promotions.
The package typically includes the Ledger Nano X device itself, a USB-C cable for connectivity, three recovery sheets for your 24-word recovery phrase, and a getting started leaflet. This investment provides a secure element chip for protecting your digital assets.
Bottom Line
A Crypto Ledger, functioning as a hardware wallet, is an indispensable tool for anyone serious about the security and self-custody wallet of their digital assets. By keeping private keys offline within a certified secure element chip, devices like the Ledger Nano X provide unparalleled protection against cyber threats.
Understanding the importance of your 24-word recovery phrase, recognizing social engineering tactics, and using the Ledger Live application’s Genuine Check feature are critical for comprehensive security. This guide has explored the fundamental principles, advanced features, and practical steps to manage digital assets securely, empowering users to navigate the web3 ecosystem with confidence.
Ultimately, a Ledger represents a commitment to personal private key ownership and robust cold storage solution.
Key Takeaways
- A Crypto Ledger is a hardware wallet that stores private keys offline for maximum security.
- The Ledger Nano X supports over 5,500 digital assets and offers Bluetooth connectivity for convenience.
- Your 24-word recovery phrase is the master key; its secure, offline storage is paramount.
- Advanced security features like the secure element chip and passphrase provide robust protection against sophisticated attacks.
- Always buy from authorized retailers and use Ledger Live’s Genuine Check feature to verify your device.






