Forex trading is the exchange of currencies on a global scale. The foreign exchange market is the world’s largest financial market, processing over $7.5 trillion daily as of 2022. It operates 24 hours a day, allowing institutions and individuals to trade currencies continuously in a highly liquid environment.
Individuals trade forex to profit from currency value fluctuations, such as speculating that the Japanese yen will rise against the U.S. dollar. The forex market is decentralized and operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, giving both institutions and retail traders unmatched global accessibility.
Learn forex trading with this beginner’s guide built on factual data and proven market principles.
While understanding Forex Trading Basics is important, applying that knowledge is where the real growth happens. Create Your Free Forex Trading Account to practice with a free demo account and put your strategy to the test.
Key Takeaways
- Forex is the world’s largest market, but it’s not a get-rich-quick scheme.
- Success depends on a disciplined, strategic approach, not on luck.
- Prioritize education and understand key concepts like pips, lots, and leverage before trading.
- Always use a demo account first to practice strategies without financial risk.
- Protect your capital with effective risk management tools like stop-loss orders.
- Choose a reputable, regulated broker to ensure transparency and security for your funds.
- Master your mindset by sticking to your trading plan and avoiding emotional decisions.
- Continuously expand your knowledge by exploring advanced analysis and strategies.
What is the Forex Market and How Does it Work?
The forex market is where people trade currencies. It’s the biggest financial market in the world. Banks, governments, companies, and individuals all participate. They buy and sell currencies for business, speculation, and risk management.
- Decentralized: No central hub exists. Trades are direct, supported by brokers.
- Liquid: Huge trading volumes mean trades happen quickly with small price changes.
- Participants: Banks, companies, hedge funds, and individual traders all take part.
Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. It runs globally, starting Monday morning in Asia and closing Friday evening in New York. There is no central exchange. Trades happen through a network of computers and brokers.
Currencies are always traded in pairs. For example, in EUR/USD, one currency (EUR) is exchanged for another (USD). If the exchange rate is 1.20, it means one euro buys 1.20 U.S. dollars. These rates constantly change based on supply and demand.
It’s worth noting that the forex market influences the global economy. It sets exchange rates, impacts trade costs, and drives investment. As a trader, you can profit from these changes—but you must understand the risks.
Forex trading requires discipline. You need to learn strategies, manage risk, and follow the market closely. It’s not just about luck—it’s about skill.
What is Forex Trading?
Forex trading (FX trading) requires you to exchange one currency for another in a global marketplace. It’s the world’s largest financial market, with an average daily trading volume of foreign exchange market is $7.5 trillion as of 2022.
Confused? Okay, let us make it simpler.
When you engage in forex trading, you speculate on whether one currency, like the U.S. dollar (USD), will strengthen or weaken against another, like the euro (EUR). The most basic idea is this: you buy one currency while selling another while aiming to profit from shifts in their relative values.
For instance, if you believe the euro will rise against the dollar, you may buy EUR/USD. When the euro strengthens, you can sell it back for a profit.
Forex Trading vs Forex Investing
Forex trading and forex investing share the same marketplace. But diverge in risk, strategy, and pace, tailored to different financial goals and timelines.
In forex trading, the goal centers on short-term profits through active buying and selling of currency pairs. So, if you’re a trader, you’d aim to capitalize on smaller price movements, but it may make multiple trades in a day. Moreover, forex trading volume backs up this approach: the market sees an average daily turnover of $7.5 trillion, which reflects significant opportunities for quick, high-frequency trades. If you leverage tools like MetaTrader 4, used by 85% of traders, then you can also utilize technical indicators to anticipate price movements quickly.
On the other hand, Forex investing focuses on longer-term currency value shifts, often with a horizon of months or years. You should know that forex investors aim to benefit from larger economic trends, such as interest rate shifts and economic growth rates. Remember that it requires patience and is less reactive to daily fluctuations. In fact, long-term forex positions tend to be more stable, with the U.S. dollar involved in 88% of all trades globally due to its role as a primary reserve currency (Bank of International Settlements, 2022).
| Feature | Forex Trading | Forex Investing |
| Objective | Profit from short-term price movements | Build long-term wealth from currency value appreciation |
| Time Horizon | Short-term (seconds, minutes, hours, or days) | Long-term (months to years) |
| Focus | Frequent buying and selling of currency pairs | Holding positions for extended periods |
| Strategy | Primarily relies on technical analysis (e.g., charts, indicators) | Relies more on fundamental analysis of economic trends |
| Risk Profile | Higher risk due to frequent leverage use and market volatility | Lower risk, usually unleveraged or with lower leverage |
| Market Analysis | Focuses on price patterns, indicators, and technical setups | Evaluates economic health, interest rates, political factors |
| Capital Requirements | Lower entry (you can start small with leverage) | Higher entry as unleveraged positions require more capital |
| Use of Leverage | Commonly uses high leverage (up to 100:1 or more) | Typically limited or no leverage |
| Liquidity | High, allowing for quick entry and exit in active trading hours | Generally, less sensitive to liquidity due to a long-term approach |
| Common Strategies | Scalping, day trading, swing trading | Position trading, long-term hedging |
| Psychological Approach | Requires emotional discipline, quick decision-making | Requires patience, low-stress approach |
| Example | A trader buys EUR/USD expecting the euro to rise against the dollar by 10 pips within a few hours. | An investor buys GBP expecting it to appreciate over several months due to anticipated economic growth in the UK. |
| Ideal For | Individuals interested in active trading, frequent engagement | Those with long-term investment goals and lower time commitment |
Why do People Trade Forex?
People trade forex to benefit from its unique characteristics, which include high liquidity, leverage, and 24/5 accessibility.
- High Liquidity: The forex market’s high liquidity means participants can enter or exit a trade quickly at a fair price. The market’s immense volume ensures there is always a buyer and a seller for a particular currency pair.
- Leverage: Leverage allows traders to control a larger position with a smaller amount of capital. A 100:1 leverage ratio allows a trader to control $10,000 with only $100 of their own money.
- 24/5 Access: The forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, spanning major financial centers in Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. This round-the-clock schedule provides traders with the flexibility to trade at any time that suits their schedule.
Is Forex Trading Risky?
Yes, forex trading is risky. The main risks associated with forex trading are high volatility, scams, and overleveraging.
- Volatility: Currency prices can change rapidly and unexpectedly due to various factors, including economic data releases, political events, and central bank actions.
- Scams: The decentralized nature of the forex market makes it a target for scams. Unregulated brokers and fraudulent trading systems often prey on beginners with unrealistic promises of guaranteed returns.
- Overleveraging: Using excessive leverage is a common mistake for beginners and can lead to rapid account depletion, as even small price movements can result in a margin call or a total loss of capital.
Key Forex Trading Concepts
Successful forex trading requires understanding core concepts like pips, lot sizes, margin, and leverage. These basics form the foundation of trading decisions and help traders calculate risk, measure profits and losses, and avoid beginner mistakes.
What is a Pip in Forex Trading?
A pip (point in percentage), measures the smallest unit of price movement in a currency pair. In most pairs, one pip is equal to 0.0001 of the quoted currency. A four-digit price quote moving from 1.0800 to 1.0801 is a single pip movement. For pairs involving the Japanese yen (JPY), a pip is typically the second decimal place, or 0.01.
How Lot Size Works in Forex?
A lot is a standardized unit of measurement in forex trading that indicates the volume of a trade. A standard lot represents 100,000 units of the base currency.
- Standard Lot: 100,000 units.
- Mini Lot: 10,000 units.
- Micro Lot: 1,000 units.
- Nano Lot: 100 units.
What is Margin in Forex?
Margin is the amount of capital required to open and maintain a leveraged position. This capital is held by the broker as a security deposit to cover potential losses.
How Does Leverage Work in Forex?
Leverage is the practice of using borrowed funds to increase a trade’s size and potential returns. A leverage ratio of 50:1 means that a trader can control a position worth $5,000 with only $100 of their own capital. This is a powerful tool, but it can magnify losses as quickly as it magnifies gains.
Unrealized P/L vs Floating P/L?
Unrealized P/L, also known as floating P/L, is the profit or loss on an open position. This is a theoretical value because the trade has not been closed yet. It becomes a realized P/L only when the trade is closed and the profit or loss is credited to the account balance.
How to Start Forex Trading?
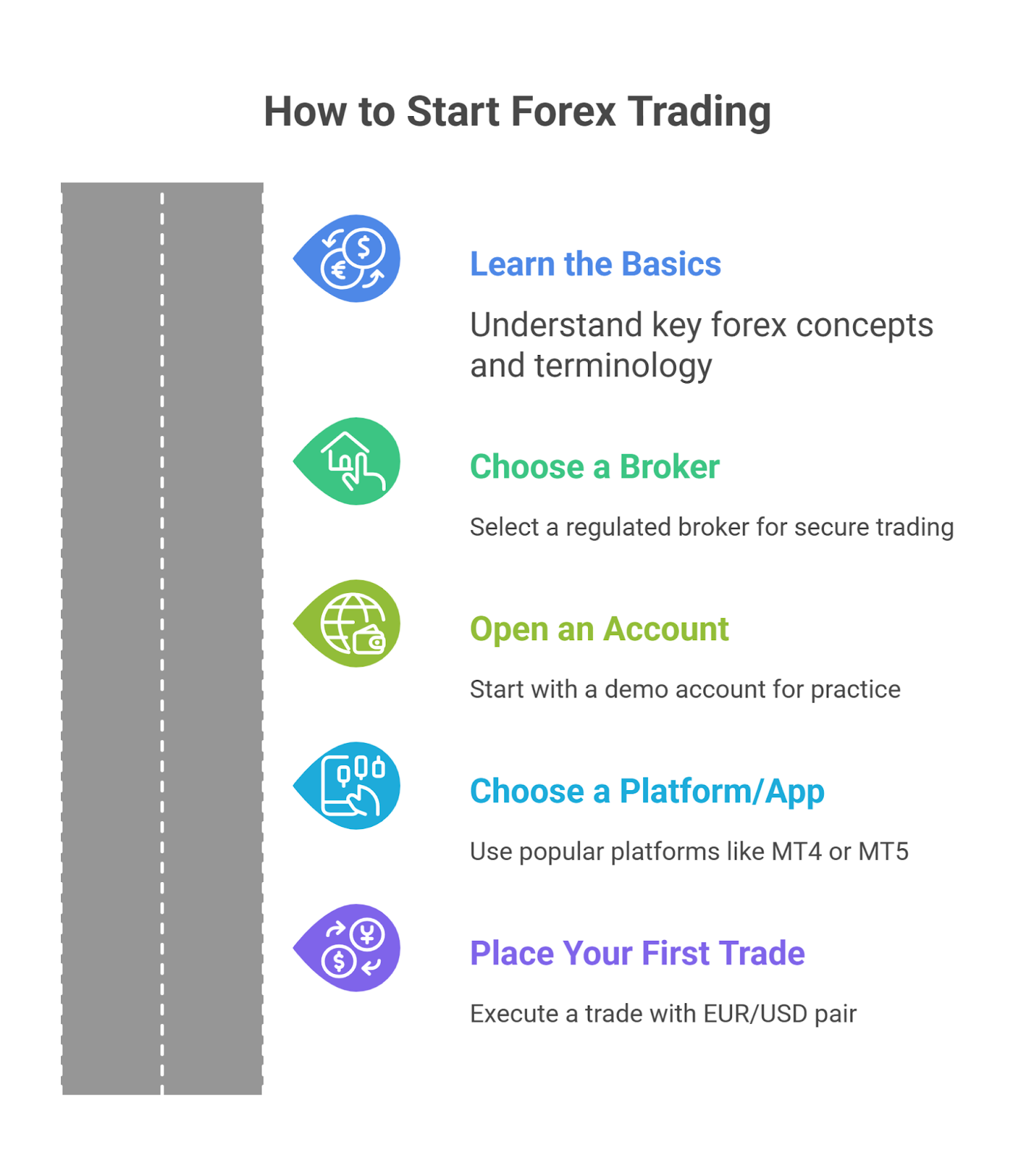
Follow this step-by-step process to progress from beginner to placing your first live trade with confidence.
Step 1: Learn the Basics
A successful forex trading career is built on a solid foundation of knowledge. Before you start, you must understand key concepts like currency pairs, pips, and leverage. A comprehensive understanding of forex terminology and market mechanics is crucial to making informed decisions and avoiding common mistakes.
Step 2: Choose a Broker
A forex broker is an intermediary that provides traders access to the market. Selecting a regulated broker is a non-negotiable step to protect your capital and ensure transparent trading practices. Look for brokers regulated by top-tier authorities like the FCA (UK) or the CFTC (US).
Step 3: Open an Account
Once you have chosen a broker, you need to open an account. Most brokers offer two types of accounts: a demo account and a live account. You should start with a demo account to get hands-on experience without risking any capital. A demo account simulates a real trading environment, allowing you to test strategies and familiarize yourself with the platform.
Step 4: Choose a Platform/App
A trading platform is the software you use to execute trades. The most popular platforms for beginners are MetaTrader 4 (MT4) and MetaTrader 5 (MT5). These platforms offer a range of tools, including charts, technical indicators, and automated trading features.
Step 5: Place Your First Trade (Example with EUR/USD)
After practicing on a demo account, you are ready to place your first trade. Here is a step-by-step example using the EUR/USD pair:
- Analyze the market: Based on your analysis, you believe the euro will strengthen against the U.S. dollar.
- Open an order: On your trading platform, you open a new order for the EUR/USD pair.
- Choose your lot size: You select a micro lot (1,000 units) to minimize risk.
- Set your stop-loss and take-profit: You place a stop-loss order at a specific price to limit potential losses and a take-profit order to lock in your desired gains.
- Execute the trade: You click the “Buy” button, and your trade is placed. You now have a long position on EUR/USD.
Ready to Elevate Your Trading?
You have the information. Now, get the platform. Join thousands of successful traders who use Volity for its powerful tools, fast execution, and dedicated support.
Create Your Account in Under 3 MinutesTypes of Forex Markets
Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week. Major trading sessions span across global financial centers in New York, London, Tokyo, and Sydney, which ensures that the market moves round-the-clock.
Let’s take a look at major types of forex markets:
Spot Market
The spot market is where transactions happen “on the spot”. It is the most direct and popular way to trade forex. Here, you buy or sell currency pairs based on the current exchange rate, with an immediate settlement.
For instance, say you believe the Euro (EUR) will strengthen against the U.S. dollar (USD). You could buy EUR/USD in the spot market and, if the Euro’s value rises, you can sell it back for a profit.
This market is ideal for you if you prefer quick, short-term trades.
It is worth noting that spot transactions account for $2.1 trillion in daily volume, which makes it the most liquid part of the forex market.
Forwards and Futures Markets
In the forwards market, you agree on a specific exchange rate and a future date to complete the transaction. This approach lets you lock in rates, which help you manage potential price swings.
Let’s say you’re an international business expecting to receive payment in a foreign currency in three months. Now, in order to avoid currency fluctuations affecting your profits, you could enter a forward contract to exchange that currency for your own at today’s rate, on a future date. This strategy is commonly used by corporations and institutions.
You should know that the forwards market trades around $1.1 trillion daily, providing a protective approach for traders who want to avoid currency risks.
Forex Trading Styles & Strategies
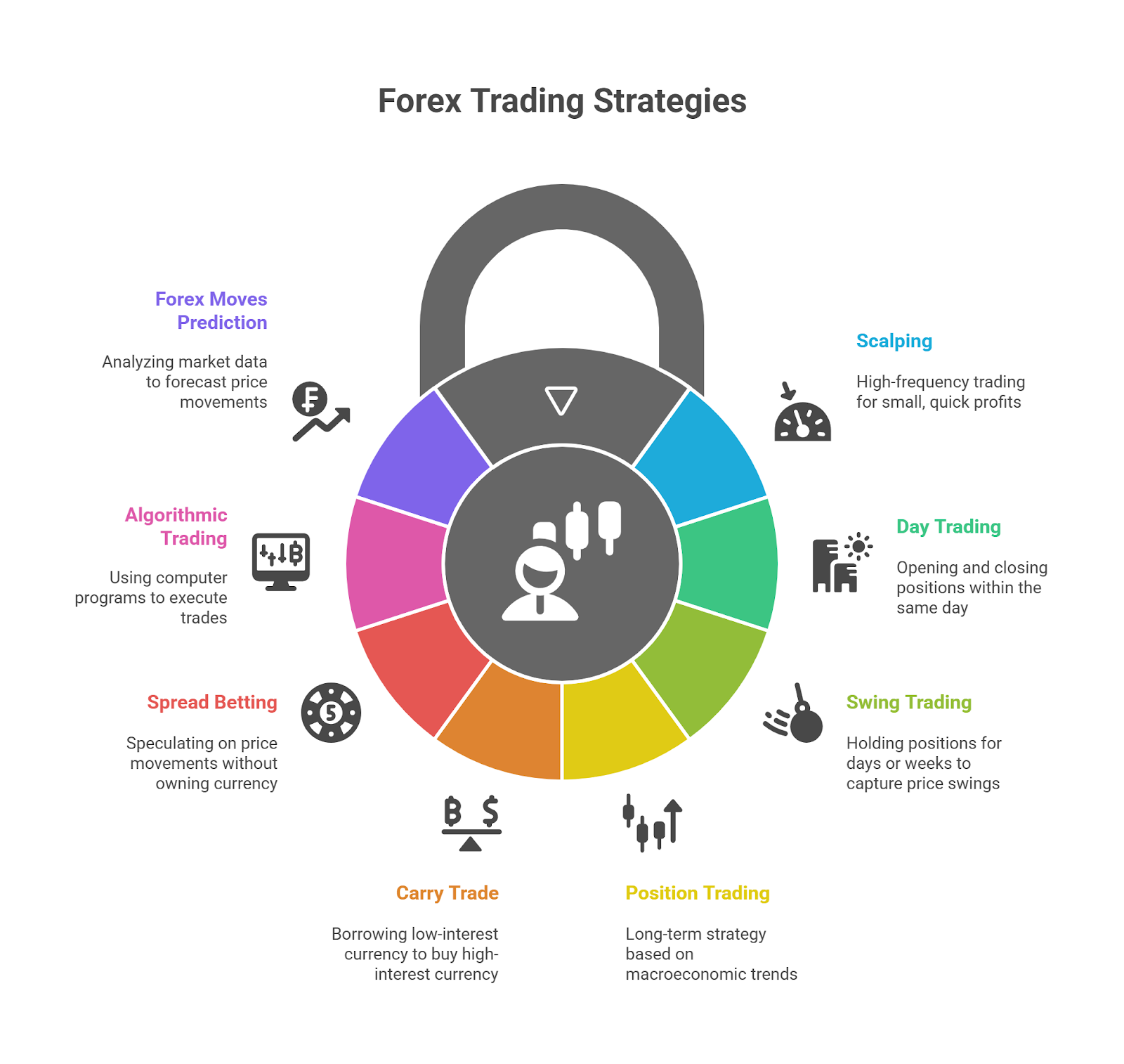
Forex traders use different strategies depending on their goals, risk tolerance, and time commitment. Below are the 8 main forex trading styles and strategies you must understand.
1. Scalping
Scalping is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders place multiple trades within seconds or minutes to profit from very small price changes. Scalpers rely on speed, tight spreads, and discipline to accumulate small gains that add up over time.
2. Day Trading
Day trading involves opening and closing all positions within the same trading day to avoid overnight risk. Day traders hold trades for minutes to hours, using technical analysis and intraday patterns to capture short-term price movements.
3. Swing Trading
Swing trading is a medium-term style where traders hold positions for several days or weeks to capture price swings. Swing traders use a mix of technical indicators and fundamental analysis to identify trend reversals and continuation patterns.
4. Position Trading
Position trading is a long-term forex strategy where traders hold positions for weeks, months, or even years. Decisions are based on macroeconomic trends, interest rate policies, and long-term technical signals, making it suitable for patient traders with higher capital.
5. Carry Trade
Carry trade is a strategy where traders borrow a currency with a low interest rate and use it to buy a currency with a higher interest rate. Profits come from the interest rate differential, making carry trades more effective in stable markets with clear monetary policy trends.
6. Spread Betting
Spread betting is a method of speculating on forex price movements without owning the underlying currency. Traders bet on whether a currency pair will rise or fall, and profits or losses depend on the size of the price movement. It is popular in regions like the UK due to tax advantages.
7. Algorithmic Trading
Algorithmic trading, or automated trading, uses computer programs and algorithms to execute trades based on predefined criteria. These systems can scan multiple currency pairs, manage risk, and execute trades faster than manual trading.
8. Forex Moves Prediction Methods
While not a strategy by itself, predicting forex moves is essential. Traders use:
- Fundamental analysis (economic news, GDP, inflation, interest rates).
- Technical analysis (price charts, moving averages, candlestick patterns).
- Sentiment analysis (market positioning and trader behavior).
Technical & Fundamental Analysis Basics
Understanding fundamental analysis and technical analysis is essential in forex trading. These two approaches help traders evaluate currency movements from different perspectives—economic drivers and market behavior.
What is Fundamental Analysis in Forex?
Fundamental analysis studies how economic, political, and social factors influence currency prices. It helps traders understand the why behind market movements.
Key indicators include:
- Interest rates set by central banks, which directly impact currency strength.
- GDP growth and overall economic performance, signaling economic stability.
- Employment reports such as the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP), which often trigger sharp short-term volatility.
Stronger economic conditions usually support a stronger currency, while weak data can lead to depreciation.
What is Technical Analysis in Forex?
Technical analysis examines past price movements to forecast future market behavior. Instead of focusing on economic news, it looks for patterns and signals in price data.
Traders use tools such as:
- Price charts (candlestick, bar, and line) to visualize market movement.
- Support and resistance levels where price historically bounces or breaks.
- Indicators like moving averages or RSI to measure momentum and trend strength.
Technical analysis is less about why prices move and more about identifying the best entry and exit points.
How Traders Use Both Analysis Together?
Successful forex traders often combine fundamental and technical analysis:
- Use fundamentals to determine the long-term direction of a currency (e.g., USD strength from rising interest rates).
- Use technicals to time entries and exits (e.g., waiting for a breakout above resistance to buy).
Forex Technical Indicators Beginners Should Know
Technical indicators fall into three main categories: trend, momentum, and volatility. Below are the essential ones beginners should know, with links to detailed guides for each.
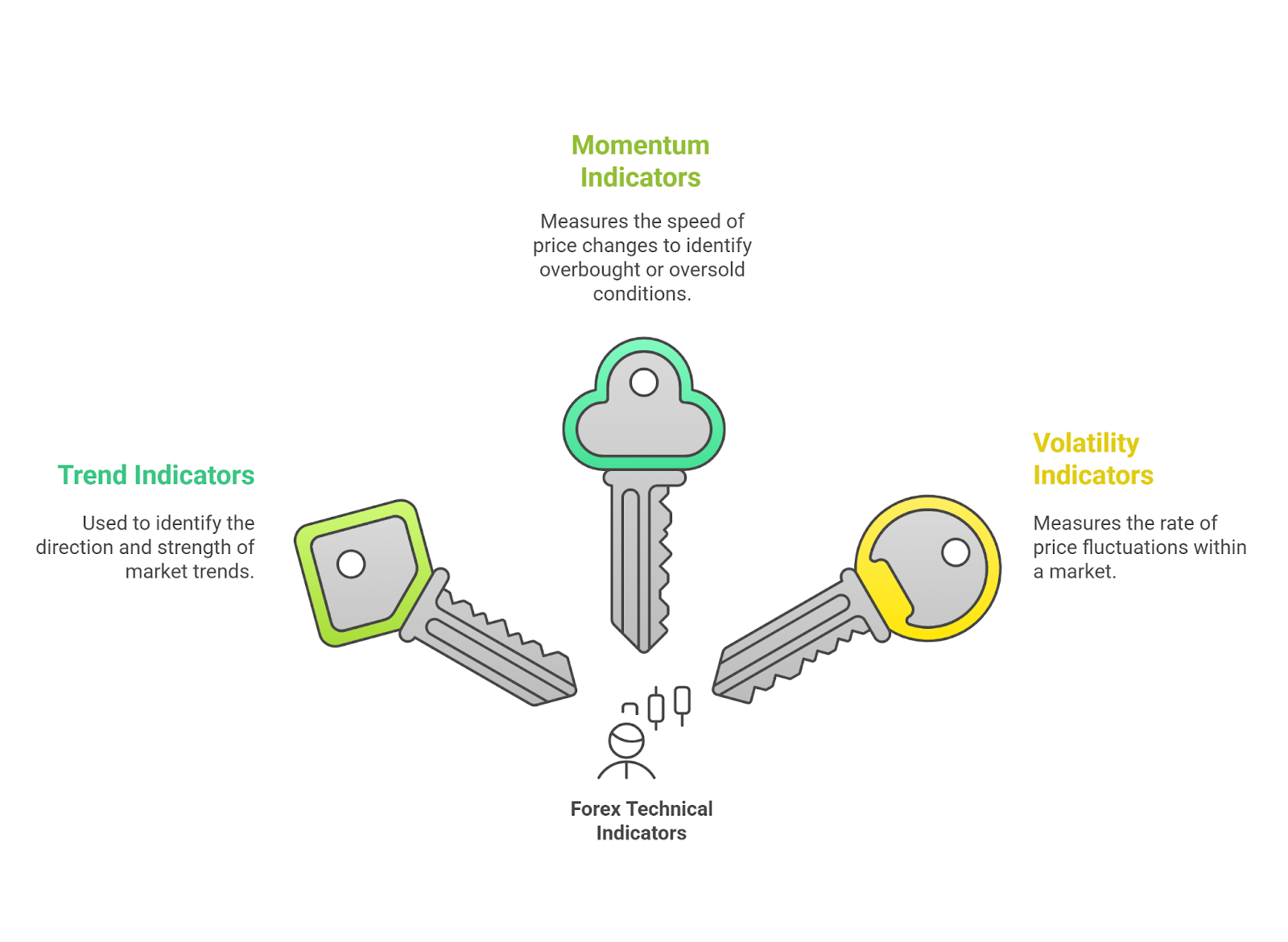
Trend Indicators
Trend indicators are used to identify the direction and strength of a market trend.
- Simple Moving Average (SMA) – Smooths price data to show whether the market is trending up or down.
- Exponential Moving Average (EMA) – A faster-reacting moving average that gives more weight to recent prices.
- Ichimoku Kinko Hyo: This is a comprehensive indicator that provides trend direction, support and resistance levels, and momentum.
- Parabolic SAR: This indicator is used to identify potential trend reversals and provides entry and exit signals.
Momentum Indicators
Momentum indicators measure the speed of price changes to identify overbought or oversold conditions.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): The RSI is an oscillator that measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions.
- Stochastic Oscillator: The Stochastic Oscillator compares a closing price to its price range over a given period to indicate momentum.
- Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): The MACD is a trend-following momentum indicator that shows the relationship between two moving averages.
- Average Directional Index (ADX): The ADX is a momentum indicator used to quantify the strength of a trend.
Volatility Indicators
Volatility indicators measure the rate of price fluctuations within a market.
- Bollinger Bands: Bollinger Bands consist of a central moving average and two outer bands that adjust to market volatility. They can identify periods of high and low volatility.
- Fibonacci Retracement: This tool identifies potential support and resistance levels where a price retracement may end before continuing in the original direction.
- Fibonacci Extensions: This tool identifies potential price targets or areas where a trend might reverse after a retracement.
Indicators are guides, not guarantees. Many traders combine them for confirmation—such as using RSI to check momentum while relying on Moving Averages for trend direction.
What Are the Main Types of Forex Charts?
Forex traders use three primary chart types to visualize currency movements. Each chart has a distinct style and reading method, providing unique insights into market behavior.
1. Line Chart
A line chart connects the closing prices of a currency pair over a specific period with a single line. This chart type is the most straightforward, making it ideal for beginners who want a clear overview of the general price movement.
The slope of the line reveals the trend: an upward slope indicates a bullish trend, while a downward slope signals a bearish trend. A line chart can also be used to identify long-term price trends.
2. Bar Chart (OHLC)
A bar chart, also known as an OHLC (Open-High-Low-Close) chart, provides more information than a line chart by displaying four key prices for each period.
- The vertical line of the bar shows the highest and lowest prices reached during the period.
- The horizontal tick on the left represents the opening price.
- The horizontal tick on the right represents the closing price.
Bar charts are useful for understanding price movement and volatility within each trading period. The length of the bar indicates the level of volatility.
3. Candlestick Charts
A candlestick chart uses colored “candles” to visually represent the Open, High, Low, and Close prices for a given period. This is the most widely used chart type in forex trading today due to its visual clarity and rich information.
- The body of the candle shows the range between the opening and closing prices.
- The wicks (or shadows) extending from the body show the highest and lowest prices.
- A bullish candle (green or white) indicates that the closing price was higher than the opening price.
- A bearish candle (red or black) indicates the opposite.
For an in-depth comparison of chart types, check out our guide on Line vs. Bar vs. Candlestick Charts, where we break down their features and differences in detail.
What Are Popular Candlestick Patterns?
Candlestick patterns are specific formations of one or more candlesticks that can signal a potential price reversal or continuation.
- Doji: A doji has a very small or non-existent body, indicating indecision in the market.
- Engulfing: A large candlestick that “engulfs” the body of the previous, smaller candlestick, often signaling a strong reversal.
- Hammer: A bullish reversal pattern with a long lower shadow and a small body.
- Hanging Man: A bearish reversal pattern with a long upper shadow and a small body.
- Shooting Star: A bearish reversal pattern with a long upper shadow and a small body.
- Morning Star: A three-candlestick pattern signaling a bullish reversal at the bottom of a downtrend.
- Evening Star: A three-candlestick pattern signaling a bearish reversal at the top of an uptrend.
- Three White Soldiers: A bullish reversal pattern consisting of three consecutive long-bodied candlesticks.
Important Chart Patterns Every Trader Should Know
Chart patterns are specific formations that appear on price charts and can signal future price movements. Learning to identify these charts helps traders understand broader market behavior.
- Head & Shoulders: A bearish reversal pattern consisting of a peak (shoulder), a higher peak (head), and a lower peak (shoulder).
- Double Top/Bottom: A double top is a bearish reversal pattern, and a double bottom is a bullish reversal pattern. Both indicate a strong level of support or resistance.
- Cup & Handle: A bullish continuation pattern resembling a “cup” and a downward-sloping “handle”.
- Trendlines: Trendlines are straight lines drawn on a chart that connect a series of highs or lows to indicate the direction of a trend.
- Pivot Points: Pivot points are technical indicators used to determine potential support and resistance levels in a market.
Risk Management & Psychology in Forex
Risk management and psychology are two of the most critical components of successful forex trading. Both are essential for long-term success, as a disciplined approach is the primary difference between profitable and unprofitable traders.
What Is Risk Management in Forex?
Risk management is the process of minimizing potential losses in trading. It is one of the most critical aspects of trading successfully.
- Stop Loss: A stop-loss order is an automatic command that closes a trade at a predetermined price to prevent further losses.
- Risk/Reward Ratio: This ratio compares the potential profit of a trade to the potential loss. A 2:1 risk/reward ratio means that for every $1 you risk, you stand to gain $2.
- Position Sizing: This involves determining the appropriate lot size for a trade based on your risk tolerance and account size.
What are Common Risks in Forex Trading?
Several common risks exist in forex trading, with a key factor being the market’s highly leveraged and volatile nature. These risks are not limited to financial loss but also include challenges related to brokers, trading platforms, and the trader’s own psychology.
- Drawdown: A drawdown is the peak-to-trough decline in an investment account during a specific period.
- Liquidity: In risk management, liquidity refers to the ability to exit a trade at a fair price without significant delay or slippage.
- Sentiment: Market sentiment refers to the overall feeling or tone of a market.
How to Master the Trader Mindset?
Forex trading demands a disciplined mindset. Emotional challenges often lead to impulsive trades and costly mistakes.
- Fear: Fear can cause a trader to close a profitable position too early, limiting their gains.
- Greed: Greed can cause a trader to hold a losing position too long, hoping for a turnaround, or to overtrade to chase losses.
- Discipline: A disciplined trader sticks to their trading plan, regardless of emotions, and consistently applies risk management rules.
Next Steps – From Beginner to Advanced Forex Trader
Moving from beginner to advanced trading means more than knowing the basics. It’s about deepening your knowledge, using advanced tools, and developing a disciplined approach that turns theory into consistent practice.
Deepen Your Market Knowledge
Moving beyond the basics means understanding the forces that drive price movements. Focus on these key concepts:
- Elliott Wave Theory: Learn to identify recurring wave patterns in market prices. This will help you anticipate trend reversals and continuation points.
- Dollar Smile Theory: Understand how the U.S. dollar reacts in both strong economic periods and global downturns to improve your currency predictions.
- Commitment of Traders (COT) Report: Analyze the weekly positions of institutional and retail traders to gauge market sentiment and potential turning points.
- Algorithmic and Automated Trading: This involves using computer programs to execute trades based on predefined rules and algorithms, which can lead to faster execution and more stable outcomes by minimizing emotional decision-making.
- Hedging: Hedging is a strategy where traders open multiple positions to protect against unfavorable price movements.
- Carry Trades: A carry trade involves borrowing a low-interest-rate currency to buy a high-interest-rate currency to profit from the interest rate differential.
- Intermarket Analysis: This involves analyzing the relationships between different markets and assets to identify trading opportunities. Understanding how factors like commodity prices or stock markets correlate with currency movements can provide a more comprehensive view of the market.
- Nonfarm Payrolls (NFP) Trading: This is an advanced strategy focused on trading the release of the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls report, which often creates significant market volatility and trading opportunities.
- Harmonic Patterns: Harmonic patterns are specific geometric shapes that form on a price chart and are used to predict future price movements. They are considered an advanced form of technical analysis.
Equip Yourself with Advanced Tools
The right tools are essential for advanced strategy execution and risk management. They help traders analyze the market, manage risk, and automate processes.
- Trading Calculators Use these tools to determine essential trade parameters, such as pip values, lot sizes, and margin requirements before entering a position. For example, a Forex Profit Calculator can help you determine the potential profit or loss of a trade based on your entry and exit points.
- Backtesting Platforms Apply your strategies to historical data to see how they would have performed in real market conditions. This helps you validate your strategy before risking capital. You can explore a Forex Backtesting Tracker to log and analyze your backtesting results.
- Economic Calendar Track key economic events, central bank announcements, and geopolitical developments that can impact currency prices. This is crucial for fundamental analysis.
- Forex News Aggregators These platforms pull news from various financial sources in real-time. They are essential for staying on top of market-moving events and news releases, which can cause significant price swings. Some popular aggregators include Investing.com and Myfxbook.
- Sentiment Analysis Tools Tools that analyze the positioning of institutional traders, such as the Commitment of Traders (COT) Report, can help you gauge market sentiment and identify potential turning points. You can access COT data directly from the CFTC website.
- Automated Trading Platforms For advanced traders, automated trading platforms and algorithms can execute trades based on predefined rules, which helps eliminate emotional decision-making. These platforms allow for faster execution and around-the-clock trading. Examples include MetaTrader 4/5 and cTrader.
Apply and Refine Your Strategies
Theory and tools are only useful when put into practice:
- Start by demo trading advanced strategies using historical insights and your tools.
- Keep a trading journal to track decisions, mistakes, and lessons learned.
- Gradually transition to live trading with a well-defined risk management plan.
Continuously Learn and Adapt
The forex market evolves constantly, so staying ahead requires ongoing education:
- Follow market analysis from reputable sources.
- Explore niche trading strategies like hedging, carry trades, or algorithmic trading.
- Attend webinars, read advanced guides, and engage in trader communities to exchange ideas.
By following this roadmap, you move deliberately from a beginner understanding of forex to a confident, advanced trader capable of making informed decisions under varying market conditions.
Turn Knowledge into Profit
You've done the reading, now it's time to act. The best way to learn is by doing. Open a free, no-risk demo account and practice your strategy with virtual funds today.
Open a Free Demo AccountBottom Line
Forex trading is a rewarding but challenging endeavor that requires a structured approach. It is not a get-rich-quick scheme; long-term success depends on a disciplined strategy and a deep understanding of market fundamentals and risks. By prioritizing education, mastering risk management, and consistently refining your approach, you can build a solid foundation to navigate the world’s largest financial market with confidence.






