Forex spread betting lets traders speculate on currency price movements without owning the asset. It offers flexibility, tax advantages in some regions, and the potential for profit in rising or falling markets. This guide explains how it works, the strategies involved, and the key facts you need for informed trading.
Key Takeaways
- Forex spread betting lets you speculate on the direction of currency prices without owning the actual asset.
- In the UK and Ireland, profits from spread betting are tax-free and exempt from Capital Gains Tax.
- You place a stake per point of movement, and your profit or loss is that stake multiplied by how many points the market moves.
- The primary cost of a trade is the spread, which is the difference between the buy (ask) and sell (bid) prices offered by the broker.
- The biggest risk is that leverage magnifies both profits and losses, meaning you can lose more than your initial deposit.
- Always use stop-loss orders and risk management rules, like risking no more than 2% of your capital on a single trade.
What is Forex Spread Betting?
Spread betting is a type of speculative trading that allows an individual to bet on the future direction of a market, such as the foreign exchange market, without buying or selling the actual currency. This form of trading is popular because in the UK and Ireland, profits from spread betting are considered gambling winnings and are exempt from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty. A forex spread bet involves two prices: a bid price and an ask price. The difference between these two prices is known as the spread.
- Spread Betting: A financial derivative where you speculate on market movements without asset ownership.
- Foreign Exchange Market: The global market for trading currencies, known for its high liquidity and volatility.
- Leverage: This mechanism allows a trader to control a large position with a small amount of capital, amplifying both potential profits and losses.
- Pip: A pip is the smallest unit of price movement for a currency pair. It is the fourth decimal place in most pairs.
- Bid Price: The price at which a market maker is willing to buy a currency pair.
- Ask Price: The price at which a market maker is willing to sell a currency pair.
How Does Forex Spread Betting Work?
To understand how forex spread betting works, you must first understand a few key concepts, including bid and ask prices, the spread, margin, and stake size. A trader opens a position, either “long” (betting on a price increase) or “short” (betting on a price decrease), with a specific stake size per point of movement, known as a pip.
Going Long in Spread Betting
A long position is a bet that the value of a currency pair will increase. For example, a trader who believes the EUR/USD will appreciate would “go long.” If the price rises, the trader makes a profit; if it falls, the trader incurs a loss.
Going Short in Spread Betting
A short position is a bet that the value of a currency pair will decrease. This is also known as a short sale. A trader who expects the EUR/USD to depreciate would “go short” and profit from the price decline.
Understanding the Spread
The Spread is the difference between the bid and ask prices of a currency pair and represents the cost of the trade paid to the broker. The size of the spread is heavily influenced by market liquidity and volatility. During periods of high market liquidity, like when major financial centers are open, spreads are generally narrower. Conversely, spreads can widen significantly during periods of low liquidity, such as overnight, or high volatility, like during major news announcements.
What is Leverage in Spread Betting?
Leverage allows a trader to control a large position with a small amount of capital. It is a tool for capital efficiency that magnifies both potential profits and potential losses. For example, with 100:1 leverage, a trader can control a £10,000 position with only £100 of their own capital.
What is Margin in Spread Betting?
Margin is the capital you must deposit with a spread betting provider to open and maintain a leveraged position. This amount is typically a percentage of the total position size and acts as a security deposit for the broker. There is an initial margin to open the trade and a maintenance margin to keep it open, with specific requirements varying by broker.
Example of a Forex Spread Betting
Consider a EUR/USD spread bet to understand the mechanics:
- Currency Pair: EUR/USD
- Bid/Ask Price: 1.10250 / 1.10260
- Spread: 1 pip
- Stake Size: £5 per pip
- Position: Go long (buy) at 1.10260
Profit Scenario: The EUR/USD price rises to 1.10300. The trader closes the position at the new bid price of 1.10290. The profit is calculated as the difference in pips (1.10290 – 1.10260 = 3 pips) multiplied by the stake size (£5), for a total profit of £15.
Loss Scenario: The EUR/USD price falls to 1.10200. The trader closes the position at the new bid price of 1.10190. The loss is the difference in pips (1.10260 – 1.10190 = 7 pips) multiplied by the stake size (£5), for a total loss of £35.
Types of Forex Spread Betting Trades
There are several types of forex spread betting trades, primarily defined by their duration. These include Daily Funded Trades and Forward Trades.
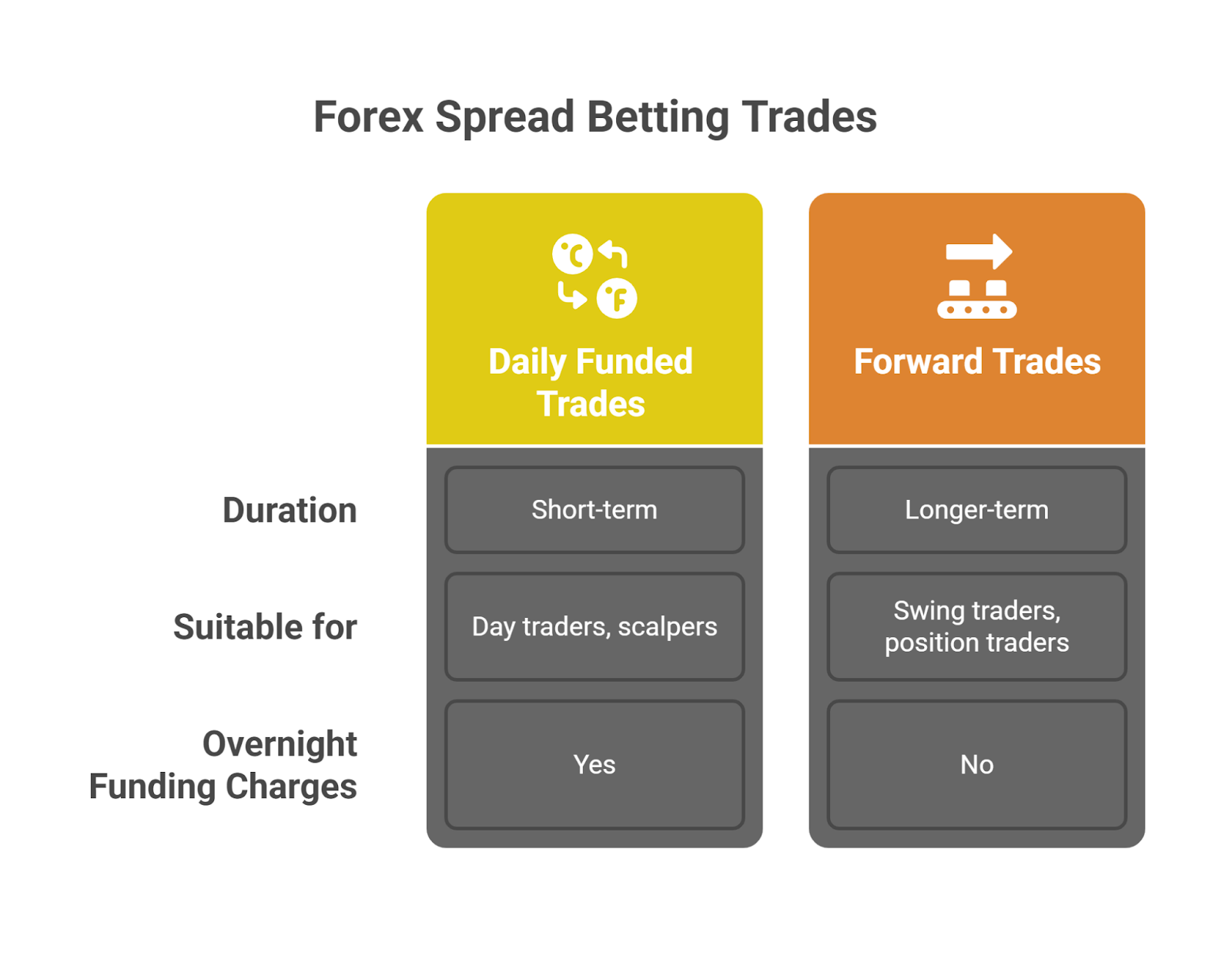
What are daily funded trades?
Daily Funded Trades (DFTs) are short-term spread bets that are typically held for a single day. They are a popular choice for day traders and scalpers. If a DFT is held overnight, a small financing fee is applied to the position.
What are forward trades?
Forward Trades are longer-term spread bets with a predetermined expiration date. They are suitable for swing traders and position traders who plan to hold positions for weeks or months. Unlike DFTs, forward trades do not incur overnight funding charges, as the cost of financing is already built into the spread.
Main Features of Forex Spread Betting
Forex spread betting is defined by several key features:
- Spread: The cost of the trade, which is the difference between the bid and ask price.
- Bet Size: The amount of money a trader risks per pip of movement. For example, a bet size of £10 means a £10 profit or loss for every 1-pip movement in the market.
- Duration: The length of time a position is held, which can range from seconds (scalping) to months (position trading).
- Expiration Date: The date on which a forward spread bet automatically closes.
Pros and Cons of Forex Spread Betting
Forex spread betting offers unique advantages and drawbacks that every trader should weigh before entering the market. While it can be a flexible and tax-efficient trading method, it also comes with risks that can lead to significant losses.
- Tax-Free Profits (UK & Ireland) – In the UK and Ireland, profits from spread betting are exempt from Capital Gains Tax and Stamp Duty, offering a clear financial advantage over many other investment vehicles.
- Market Flexibility – Traders can profit from both rising and falling markets, making it possible to find opportunities in bullish and bearish conditions.
- Low Entry Cost – As a leveraged product, spread betting requires only a fraction of the trade value as margin, allowing traders to control larger positions with smaller capital outlays.
- High Leverage Risk – While leverage can amplify gains, it can also magnify losses, potentially exceeding your initial deposit.
- Volatility Risk – The forex market is prone to sharp, unpredictable price movements that can result in rapid losses.
- Gap Risk – Price gaps, often occurring overnight or after weekends, can bypass stop-loss orders and lead to losses larger than anticipated.
- Counterparty Risk – Spread betting contracts are made directly with your broker, not the open market, meaning your trading success depends partly on the broker’s integrity and regulation.
Forex spread betting can be a powerful trading tool when combined with sound strategy and strict risk management. However, traders should fully understand the risks—especially those linked to leverage—before committing capital.
Risk Management in Forex Spread Betting
Effective risk management is crucial for success in spread betting. There are several tools and strategies to mitigate potential losses:
- Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order automatically closes a position when it reaches a predetermined price, helping to limit potential losses.
- The 2% Rule: A common risk management principle is to never risk more than 2% of your total trading capital on a single trade. This numerical approach helps prevent emotional overtrading and protects the trading account from significant drawdowns.
- Take-Profit Orders: A take-profit order closes a position when it reaches a specific profit target, helping to lock in gains.
- Diversification: Spreading your capital across different currency pairs can help reduce the risk of a single market event negatively impacting your entire portfolio.
- Position Sizing: Experts recommend risking only a small percentage of your total trading capital on any single trade, such as 1-2%.
Forex Spread Betting vs. CFD Trading
Forex spread betting and CFD (Contract for Difference) trading are both popular financial derivatives for speculating on market price movements. However, they have distinct differences, particularly in their regulatory oversight and tax implications. CFDs are often seen as more of a direct investment vehicle, whereas spread betting is regulated as a form of gambling in the UK.
| Feature | Forex Spread Betting | CFD Trading |
| Asset Ownership | You do not own the underlying asset. | You do not own the underlying asset. |
| Taxation | Tax-free in the UK and Ireland. | Subject to Capital Gains Tax in the UK. |
| Cost Structure | Cost is included in the spread. | May involve spreads, commissions, and overnight fees. |
| Expiration | Daily funded trades have no expiration; forward trades have a set expiration. | No set expiration date. |
| Regulation | Regulated under gambling law in the UK. | Regulated as a financial product in the UK. |
Forex Spread Betting vs. Binary Options
Forex spread betting and Binary Options are both forms of speculative trading, but they differ significantly in their risk and reward structures:
- Binary Options: This derivative has a fixed payout and a fixed risk. A trader simply bets whether an asset’s price will be above or below a certain level at a specific expiration time. This structure can be seen as having a higher counterparty risk as the broker often acts as the counterparty to the trade.
- Forex Spread Betting: This derivative has a variable risk and reward. The profit or loss is directly proportional to the price movement of the underlying asset. Spread betting offers more flexibility, as positions can be closed at any time before expiration.
Forex Spread Betting Strategies for Success
There are several proven strategies that traders use to find success in forex spread betting:
- Trend Following: A strategy where traders identify and follow a prevailing market trend. This involves entering a long position in an uptrend and a short position in a downtrend.
- Range Trading: This strategy works best in a ranging market with no clear trend. Traders look for support and resistance levels to buy at the bottom of the range and sell at the top.
- Scalping: A high-frequency strategy where traders make many small profits from minor price movements over seconds or minutes. Scalping requires fast execution speeds, a high degree of analytical capabilities, and close risk management.
- Swing Trading: This strategy involves holding a position for several days or weeks to capture a larger price swing. Swing traders use longer timeframes (H4 or D1 charts) and can afford to check in less frequently than scalpers.
- Hedging: Hedging is a risk management strategy where a trader opens a position to offset potential losses in an existing position.
Automated Forex Trading and AI in Spread Betting
Automated trading is the process of using computer programs to execute trades based on a set of predefined rules. This can be a useful tool in spread betting.
- Expert Advisors (EAs): These are programs that run on trading platforms like MT4 or MT5 to automate trade execution. EAs can follow complex algorithmic trading strategies.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI can be used to analyze vast amounts of data, recognize patterns, and make predictions about market movements. This can lead to more adaptive and sophisticated trading models with faster execution speeds.
Popular Forex Spread Betting Platforms
When choosing a spread betting platform, traders should consider several factors, including the spreads offered, available leverage, and regulatory status. Different platforms cater to different trader personas based on their features:
- MT4/MT5: MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5 are the most popular trading platforms in the world for spread betting and CFD trading. They are widely used by algorithmic traders and those using Expert Advisors (EAs) due to their robust automation capabilities.
- cTrader: Known for its fast execution and a clean user interface, cTrader appeals to scalpers and day traders who prioritize low latency and a transparent market environment.
- Broker Names: Reputable brokers offering spread betting include IG, CMC Markets, and Plus500.
Final Words
Forex spread betting is a financial derivative that offers a leveraged way to speculate on currency price movements. It provides benefits like tax-free profits in the UK, but it also comes with significant risks, primarily due to leverage. To succeed, a trader must employ robust risk management techniques and a well-defined trading strategy. It is crucial to understand the mechanisms, including the bid, ask, spread, and margin requirements, before placing a bet.






