A Forex Economic Calendar is a vital tool used by traders to track scheduled economic events, such as the U.S. Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP) report. Since these data releases often cause significant price swings and market volatility, the calendar allows traders to anticipate potential movements in currency pairs.
This guide defines the forex economic calendar, explains its importance, breaks down key events, and provides a framework for its use in trading.
While understanding Forex Economic Calendar is important, applying that knowledge is where the real growth happens. Create Your Free Forex Trading Account to practice with a free demo account and put your strategy to the test.
Key Takeaways
- The Forex Economic Calendar is a roadmap for scheduled events that create market volatility.
- Traders must focus on high-impact events like interest rate decisions, NFP, and CPI reports.
- The market’s reaction is driven by the difference between the forecast and actual data.
- Risk management, including using stop-losses and appropriate leverage, is essential when trading news.
- Checking the calendar daily is a critical habit for preparing for market movements.
What Is a Forex Economic Calendar?
A Forex Economic Calendar is a schedule of economic events that directly affect currency markets. It highlights data such as Gross Domestic Product (GDP), the Consumer Price Index (CPI), interest rates, and unemployment reports.
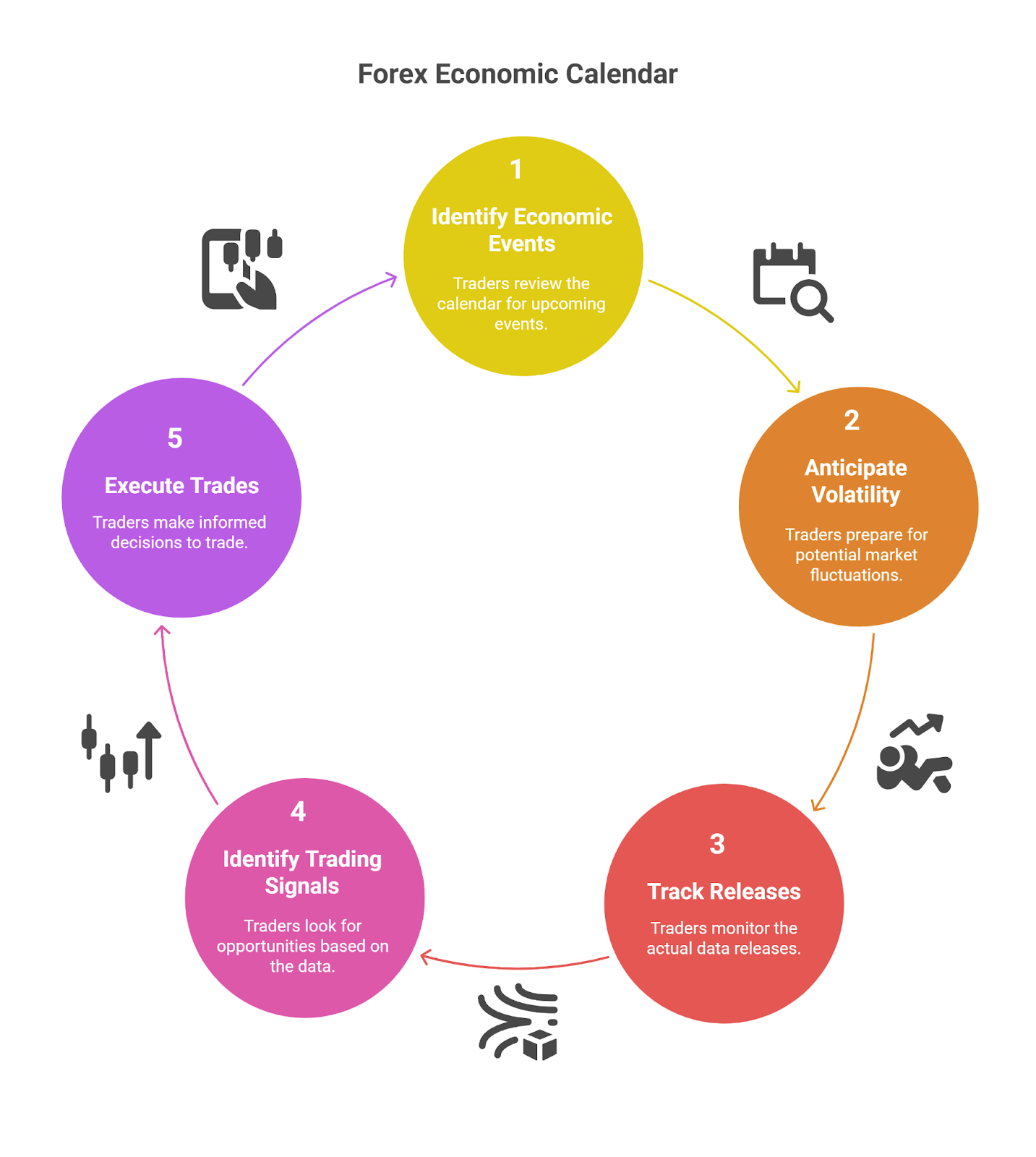
Traders use it to anticipate volatility, track central bank and government releases, and identify potential trading signals for currency pairs.
Why Is the Economic Calendar Important in Forex?
The economic calendar is important in forex trading for its utility in predicting volatility and improving risk management. Its benefits apply to all trading styles, from scalping and day trading to long-term swing trading, and it forms one of the first tools covered in Forex Trading for Beginners
- Predicting Volatility: The calendar highlights high-impact news events that typically increase market activity and liquidity. For example, the NFP report, released by the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), often causes the spread on USD pairs to widen and price action to become erratic, presenting both opportunity and risk.
- Improving Risk Management: Awareness of a major upcoming event allows traders to adjust their strategies. A trader might tighten a stop-loss, reduce leverage, or close a position entirely before a high-impact announcement to avoid adverse price movements.
- Identifying Trading Opportunities: Significant deviations between forecast and actual data can trigger strong, directional trend shifts. Traders use this “surprise” factor to enter positions that align with the new market momentum.
How to Read a Forex Economic Calendar?

To read a forex economic calendar, a trader must understand its five core components: the event time, the affected currency, the event’s description, its impact level, and the data fields.
- Date and Time: This shows when an event or data release is scheduled. Most calendars automatically convert this to a user’s local time zone to prevent confusion.
- Currency: This indicates the currency that the event will most directly affect. For example, a GDP release from Germany impacts the Euro (EUR).
- Event Description: This provides the name of the economic indicator being released, such as “Consumer Price Index (CPI) m/m.”
- Impact Level: Events are categorized by their expected market impact, typically rated as low, medium, or high. High-impact events, often marked in red, have the greatest potential to cause market volatility.
- Data Fields: Three primary data figures are provided:
- Previous: The result from the prior reporting period.
- Forecast: The consensus expectation from market analysts.
- Actual: The official figure released at the scheduled time.
The market’s reaction depends heavily on the relationship between the actual and forecast numbers. A significant difference between the two is a primary trigger for volatility.
What Are the Key Economic Events Forex Traders Must Watch?
Forex traders must watch several recurring high-impact economic events that consistently move the market. These events provide insight into a country’s economic health and influence central bank policy.
- Interest Rate and Inflation Decisions: Announcements from central banks like the Fed or ECB are the most significant market movers, directly shaping interest rate trading strategies in forex.
- Non-Farm Payrolls (NFP): Released by the U.S. BLS on the first Friday of each month, this report details job creation and directly impacts the U.S. Dollar.
- Consumer Price Index (CPI): This is a key measure of inflation. A higher-than-expected inflation rate may lead central banks to raise interest rates, strengthening the currency and often triggering scenarios described in the dollar smile theory.
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This report measures the total value of all goods and services produced by a country, serving as a primary gauge of economic health.
- Retail Sales Index: This indicator tracks consumer spending, a major driver of economic growth. A strong retail sales index often signals a robust economy.
- Consumer Confidence Index (CCI): This measures how optimistic consumers are about the economy’s health, which can influence their spending habits.
- Trade Balance: This report measures the difference between a country’s imports and exports. A surplus (more exports) can be positive for a currency.
- OPEC Reports: Meetings and reports from the Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC) influence oil prices, which impacts the currencies of oil-exporting nations like Canada (CAD) and Norway (NOK).
Ready to Elevate Your Trading?
You have the information. Now, get the platform. Join thousands of successful traders who use Volity for its powerful tools, fast execution, and dedicated support.
Create Your Account in Under 3 MinutesHow to Use the Economic Calendar for Forex Trading?
To use the economic calendar, traders integrate its data into specific strategies that combine fundamental and technical analysis. Different trading styles leverage the calendar in unique ways.
- Intraday Trading: Scalpers and day traders use high-impact events to trade volatility spikes. They often use technical analysis on lower timeframes to identify short-term entry and exit points immediately following a data release.
- Momentum and Breakout Trading: A significant deviation between forecast and actual data can cause price to break through key support or resistance levels. Momentum traders enter positions to ride the strong directional move that follows the news “surprise.”
- Swing Trading: Swing traders use economic data to confirm their bias and often cross-check it with the commitment of traders report to understand positioning behind the moves.
- Position Trading: Position traders, who hold trades for months or years, use the calendar to track major economic trends. They focus on Long-term GDP growth also interacts with fixed-income markets, making the bond yield spread a vital complementary indicator for traders.
What Is an Economic Calendar Strategy?
An economic calendar strategy is not about trading a single data release but is a comprehensive process for preparing for and reacting to market-moving events. It involves turning the calendar from a simple schedule into a dynamic part of your trading plan.
A complete economic calendar strategy includes four steps:
- Review and Identify: Check the calendar at the start of each day and week to identify all medium and high-impact events relevant to the currencies you trade.
- Filter for Importance: Use the calendar’s filtering tools to hide low-impact news and focus only on the events that have a high probability of causing volatility.
- Plan Potential Scenarios: Before a release, define how you might trade different outcomes. For example, if CPI is higher than forecast, you might expect a stronger currency unless offset by widening risk premiums—exactly the type of move explained in how risk differentials affect currencies.”
- Define Risk in Advance: The most crucial step is to decide on your risk management. This means setting your stop-loss, determining your position size, and knowing whether you will trade before, during, or after the announcement.
Mistakes to Avoid When Using an Economic Calendar
Traders must avoid four common mistakes when using an economic calendar to prevent unnecessary losses.
- Ignoring Time Zones: Failing to configure the calendar to the correct local time zone can cause a trader to miss an event or enter the market at the wrong time.
- Overreacting to Minor Events: Low-impact events rarely cause significant volatility. Reacting to this data can lead to overtrading and poor decision-making.
- Neglecting Risk Management: Trading around high-impact news without a defined stop-loss or with excessive leverage is a primary cause of large, rapid losses.
- Misinterpreting Data: A positive data release does not always strengthen a currency. The market’s reaction is based on expectations, not just the data itself. That’s why Forex sentiment analysis is often paired with calendar events to gauge psychology.
How Do You Manage Risk When Trading Economic Events?
Effective risk management when trading economic events involves four main strategies to preserve capital during periods of high volatility.
- Use Appropriate Position Sizing: Reduce your standard trade size when entering the market just before or after a high-impact news release.
- Avoid Over-Leverage: High leverage magnifies both gains and losses. Lowering leverage during news events protects against margin calls.
- Implement Stop-Loss Orders: A hard stop-loss is a non-negotiable risk management tool that defines the maximum acceptable loss on a trade.
- Recognize When Not to Trade: Sometimes the most profitable action is no action. Staying out of the market during extremely volatile events is a valid risk management strategy.
Best Practices for Using Forex Economic Calendars
The best practices for using a forex economic calendar involve incorporating it into a daily trading routine.
- Check the calendar daily: Review the schedule at the start of each trading day to identify any events that could impact your plans. This is a discipline shared by many successful Forex traders, who attribute part of their consistency to strict calendar tracking.
- Filter the calendar view: Use filters to display only high-impact events relevant to the specific currencies you trade.
- Track historical reactions: Observe how specific currency pairs have reacted to past data releases to help form expectations. For example, the US Dollar Index (DXY) often reacts sharply to NFP and CPI surprises.
- Set up alerts: Use your calendar tool to set up alerts for important upcoming events to ensure you are prepared.
What Are the Recommended Economic Calendars?
For reliable, real-time data, traders should use trusted economic calendars provided by major financial platforms. These resources offer excellent filtering tools, consensus forecasts, and historical data.
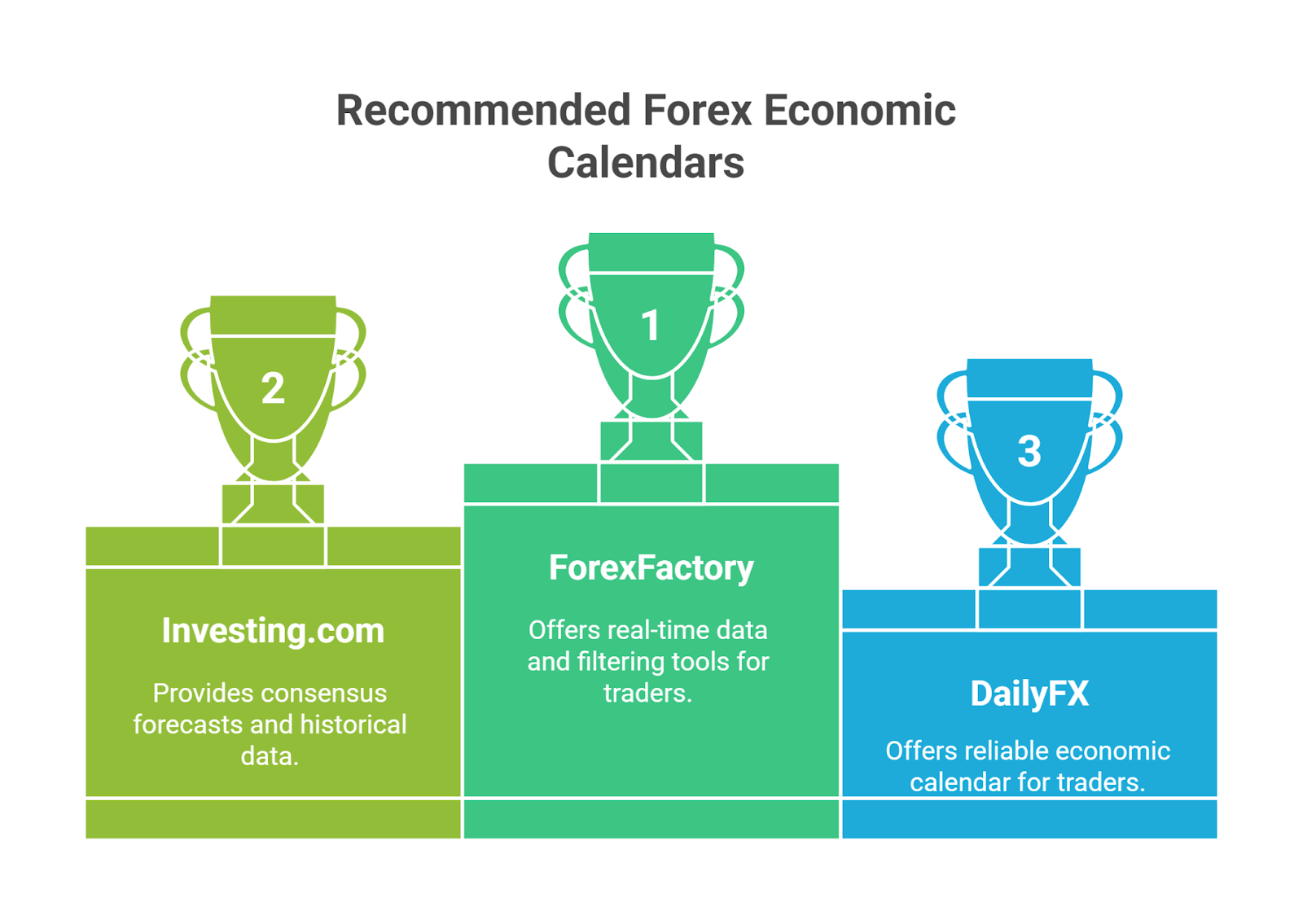
Top trusted resources include:
For primary data, traders can also refer to official sources like the International Monetary Fund (IMF) or the websites of central banks.
Turn Knowledge into Profit
You've done the reading, now it's time to act. The best way to learn is by doing. Open a free, no-risk demo account and practice your strategy with virtual funds today.
Open a Free Demo AccountBottom Line
Mastering the forex economic calendar is a key step in transitioning from a reactive to a proactive trader. This tool provides a clear schedule of events that influence market volatility and currency direction. By integrating the calendar into a daily routine, traders can improve their decision-making, enhance risk control, and better anticipate trading opportunities. Its consistent use is a hallmark of the discipline and preparation required for navigating the financial markets effectively.






